Gout, a form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, is a painful and debilitating condition. Fortunately, medications can help manage gout, reduce inflammation, and prevent future attacks. However, it’s important to understand both the benefits and the potential side effects of these medications to ensure optimal treatment. In this article, we will explore the various medications commonly prescribed for gout, how they work, and the side effects to watch out for. Whether you are experiencing your first gout flare-up or have been living with chronic gout, this guide will help you make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Understanding Gout Medications
Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid in the bloodstream, which leads to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints. These crystals cause inflammation, redness, and intense pain, typically affecting the big toe. The goal of gout treatment is to lower uric acid levels, relieve pain during acute attacks, and prevent future flare-ups. Medications are a critical component of managing this condition, and different types of drugs are used at various stages of treatment.
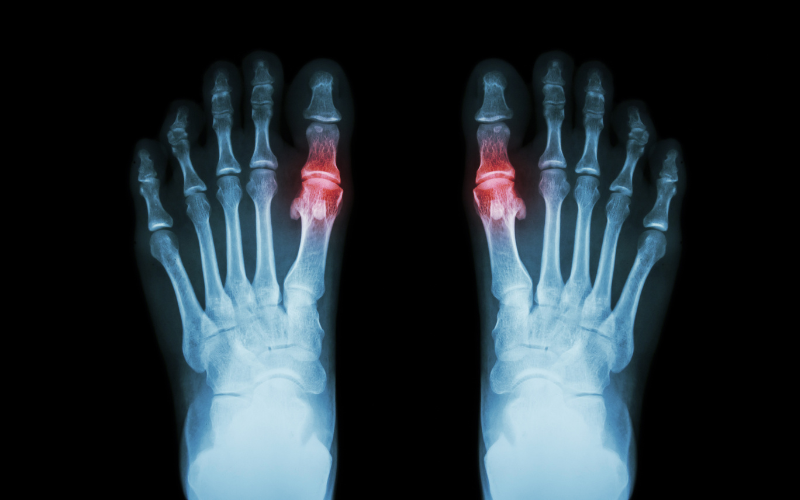
There are two main categories of medications for gout:
- Medications for acute gout attacks – These are used to alleviate the pain and swelling during a flare-up.
- Medications for long-term management – These aim to lower uric acid levels in the body to prevent recurring gout attacks.
Medications for Acute Gout Attacks
Acute gout attacks are sudden and painful, and treating them promptly is crucial to reduce discomfort and prevent further joint damage. The most common medications used for acute gout flare-ups include:
1. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and indomethacin, are often prescribed to reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling during an acute gout attack. These drugs work by blocking the enzymes responsible for inflammation, thus providing relief.
Benefits:
- Rapid pain relief during acute flare-ups
- Reduces joint swelling and redness
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach ulcers, bleeding, or indigestion
- Kidney damage with long-term use, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions
- Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes when taken in high doses or for extended periods
2. Colchicine
Colchicine is another medication commonly used to treat acute gout attacks. It works by reducing the inflammation caused by uric acid crystals in the joints, providing relief within hours to days of use.
Benefits:
- Effective at reducing pain and swelling during gout flare-ups
- Works quickly to alleviate symptoms
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Long-term use can lead to liver or kidney toxicity, especially at high doses
3. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are prescribed when NSAIDs or colchicine are ineffective or not suitable due to other health conditions. They work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation in the affected joints.
Benefits:
- Fast-acting relief from pain and inflammation
- Can be taken orally, or injected directly into the affected joint for localized treatment
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Weight gain and fluid retention
- Increased risk of infection due to immune suppression
- Long-term use can lead to osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and diabetes
Medications for Long-Term Management of Gout
While acute medications provide short-term relief, long-term management of gout focuses on reducing uric acid levels in the blood to prevent future attacks. The medications used for chronic gout include uric acid-lowering drugs and medications that help eliminate excess uric acid from the body.
1. Urate-Lowering Therapy (ULT)
ULT medications are essential for long-term gout management. These drugs help lower uric acid levels, preventing the formation of uric acid crystals and reducing the frequency of attacks. The most commonly used ULT medications are:
- Allopurinol: This medication decreases uric acid production by inhibiting the enzyme xanthine oxidase. It is typically prescribed for patients who have frequent gout attacks or who experience kidney stones due to high uric acid levels.
Benefits:
- Reduces uric acid levels in the blood
- Prevents future gout attacks and uric acid crystal formation
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Rash or skin reactions
- Gastrointestinal upset
- Potential kidney damage (requires regular monitoring of kidney function)
- Febuxostat: Similar to allopurinol, febuxostat is another xanthine oxidase inhibitor that lowers uric acid levels. It is often prescribed to patients who do not tolerate allopurinol.
Benefits:
- Effective in reducing uric acid levels
- Well-tolerated in many patients who cannot use allopurinol
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Liver enzyme abnormalities
- Nausea and headaches
- Increased risk of heart-related issues (though less common than with allopurinol)
2. Probenecid
Probenecid is a uricosuric drug that works by increasing the excretion of uric acid through the kidneys. This medication helps lower uric acid levels in the blood, preventing crystals from forming in the joints.
Benefits:
- Helps lower uric acid levels by promoting its elimination from the body
- Suitable for patients who have normal kidney function
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Kidney stones, especially if not enough water is consumed
- Headaches and gastrointestinal upset
- Rash or allergic reactions
3. Lesinurad
Lesinurad is a newer uricosuric drug often prescribed in combination with allopurinol or febuxostat. It helps increase the elimination of uric acid by the kidneys.
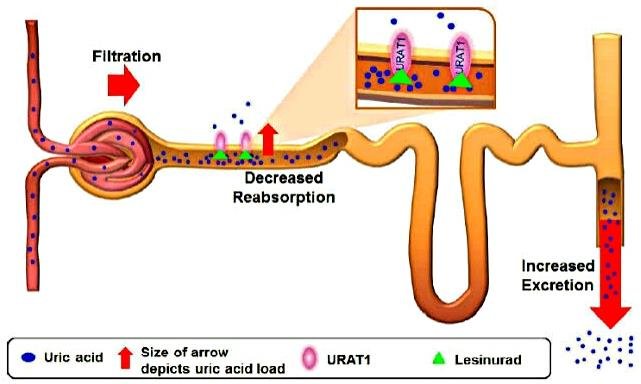
Benefits:
- Enhances the effectiveness of other urate-lowering medications
- Helps reduce uric acid levels over time
Side Effects to Watch Out For:
- Kidney-related issues, including kidney stones
- Potential for elevated blood pressure
- Nausea and diarrhea
Lifestyle Modifications to Complement Gout Medication
In addition to medications, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage gout and reduce the risk of flare-ups. These include:
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding purine-rich foods, such as red meat, shellfish, and organ meats, is crucial. Instead, focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limiting alcohol and sugary beverages can also help.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps flush uric acid from the body and prevents crystal formation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on joints and lowers the risk of gout attacks.
Conclusion
Medications play a vital role in managing gout, providing relief from acute attacks and preventing future flare-ups by lowering uric acid levels. While these medications offer significant benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks associated with long-term use. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication for gout to ensure it is the right treatment for your condition. By combining medications with healthy lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage gout and improve your overall quality of life.
Leave a Reply