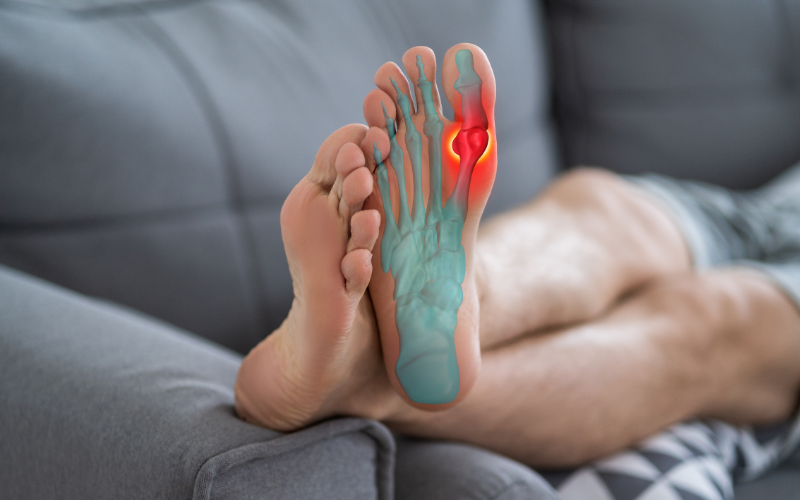
Gout, once considered a condition that only affected older adults, is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals. Traditionally associated with excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and a diet rich in purines, gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in joints, often starting in the big toe. The rising prevalence of this condition in younger people has raised concerns about lifestyle choices and their long-term impact on health. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and effective prevention strategies for gout in young people, helping them make informed choices to avoid this painful condition.
What is Gout?

Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals build up in the joints, leading to inflammation and intense pain. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks, including red meat, seafood, sugary beverages, and alcohol. When the body produces too much uric acid or is unable to excrete it efficiently, the excess uric acid can form crystals that accumulate in the joints, triggering a gout attack. This condition can cause severe pain, swelling, and redness, especially in the affected joint, making even the simplest movements excruciating.
Causes of Gout in Young People
While gout has historically been associated with older adults, it’s becoming increasingly common among young people. Several factors contribute to the rising incidence of gout in younger populations:
- Diet and Lifestyle ChoicesModern dietary habits, such as the consumption of high-purine foods and sugary drinks, have contributed significantly to the development of gout in younger individuals. Diets high in red meat, shellfish, organ meats, and processed foods are rich in purines, which increase uric acid production in the body. Additionally, sugary sodas and fruit juices can contribute to higher levels of uric acid, as can alcohol, particularly beer and spirits.
- Obesity and OverweightObesity is a major risk factor for gout, as excess weight can lead to increased production of uric acid and reduced kidney function, making it harder for the body to eliminate it. In young people, sedentary lifestyles, lack of physical activity, and poor eating habits have led to an increase in obesity rates, which in turn raise the risk of developing gout.
- Genetics and Family HistoryGenetics also play a significant role in the development of gout. If there is a family history of the condition, a young person may be more prone to developing it. Inherited genetic factors can affect the way the body processes uric acid, making some individuals more susceptible to its buildup in the joints.
- DehydrationInsufficient water intake can contribute to gout attacks. Dehydration reduces the ability of the kidneys to filter uric acid, allowing it to accumulate in the bloodstream and potentially form crystals in the joints. Many young people, particularly those with busy lifestyles, may neglect to drink enough water, unknowingly increasing their risk of gout.
- Medications and Medical ConditionsCertain medications, such as diuretics used to treat high blood pressure, and medical conditions, like kidney disease, can contribute to gout development. Diuretics can reduce the body’s ability to excrete uric acid, leading to its buildup. Additionally, conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome have been linked to higher uric acid levels and gout.
Symptoms of Gout in Young People
Gout typically presents itself through sudden, severe attacks of pain in the affected joint, often occurring at night. The following symptoms are commonly associated with gout:
- Intense joint pain: The pain often begins suddenly and is most intense within the first 12-24 hours. The big toe is commonly affected, but gout can also occur in other joints, such as the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists.
- Swelling and redness: The affected joint may become swollen, tender, and red in appearance, with the skin feeling hot to the touch.
- Limited mobility: Due to the pain and swelling, movement in the affected joint may be restricted, making it difficult to walk or perform other daily activities.
- Tophi (chronic gout): In some cases, chronic gout can lead to the formation of tophi, which are lumps of uric acid crystals under the skin. These lumps are typically found around joints and can become swollen and painful.
Prevention of Gout in Young People
While gout can be a painful and debilitating condition, it is largely preventable, especially in younger individuals. By making simple lifestyle changes, young people can significantly reduce their risk of developing gout and its complications.
- Maintain a Healthy DietOne of the most effective ways to prevent gout is by adopting a diet that helps control uric acid levels. A diet low in purines is key, as purines are broken down into uric acid. Consider the following dietary guidelines:
- Limit high-purine foods: Reduce the consumption of red meat, shellfish, organ meats, and high-fat dairy products.
- Incorporate low-purine foods: Opt for plant-based proteins, such as beans, lentils, and tofu. Whole grains, vegetables, and fruits are excellent choices.
- Avoid sugary drinks: Soda and sugary beverages can elevate uric acid levels, so replace them with water, herbal teas, or low-calorie drinks.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Beer, spirits, and excessive alcohol intake are known to increase uric acid levels, so it’s best to drink in moderation or avoid alcohol altogether.
- Stay HydratedDrinking enough water is crucial for flushing uric acid out of the body. Young people should aim to drink at least 8 glasses (2 liters) of water per day. This helps maintain kidney function and reduces the likelihood of uric acid crystals forming in the joints. Water also supports overall health and digestion, making it an essential part of any healthy lifestyle.
- Maintain a Healthy WeightObesity is a significant risk factor for gout. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can reduce the risk of developing gout. Young people should focus on staying active by engaging in activities like walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling. Strength training and resistance exercises can also be beneficial for overall health and weight management.
- Manage Stress LevelsChronic stress can contribute to inflammation in the body, potentially triggering gout attacks. Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature, can help lower stress levels and prevent gout flare-ups.
- Monitor MedicationsCertain medications, including diuretics and immunosuppressants, can raise uric acid levels. If you are taking any medication, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider about its potential impact on gout. In some cases, alternative medications may be prescribed to reduce the risk of gout development.
- Regular Health CheckupsRegular health checkups can help detect underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or kidney disease, that can increase the risk of gout. Early detection and management of these conditions can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing gout.
Conclusion
While gout may seem like a condition that primarily affects older adults, it is becoming increasingly common in young people due to modern lifestyle choices and diet. By understanding the causes and symptoms of gout, young individuals can take proactive steps to prevent this painful condition. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and managing stress levels are all essential strategies for preventing gout. Regular medical checkups and awareness of medications that may increase uric acid levels are also important in maintaining overall health. With the right preventive measures, young people can live gout-free and enjoy a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Leave a Reply