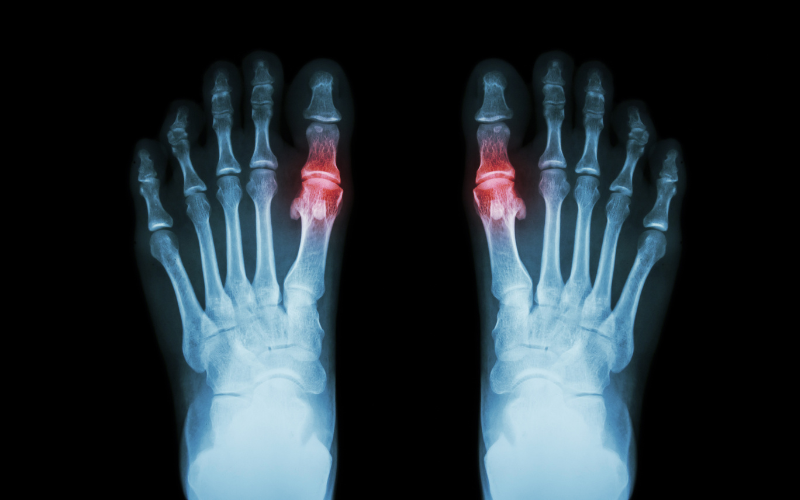
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain in the joints, typically in the big toe. It occurs when there is a buildup of uric acid in the body, which forms sharp crystals that accumulate in the joints. While genetics play a role, daily habits, such as diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices, are key factors that influence the frequency and severity of gout attacks. This article delves into how daily habits contribute to gout and offers actionable tips on how to manage and prevent gout through better lifestyle choices. By understanding the link between habits and gout, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their joint health and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
What is Gout and How Does It Develop?
Gout is a type of arthritis that results from the accumulation of uric acid in the blood, which can form crystals in the joints. These crystals lead to inflammation, pain, and swelling. The primary cause of gout is hyperuricemia, a condition where uric acid levels in the blood are too high. This can happen when the body produces too much uric acid or is unable to eliminate it efficiently.
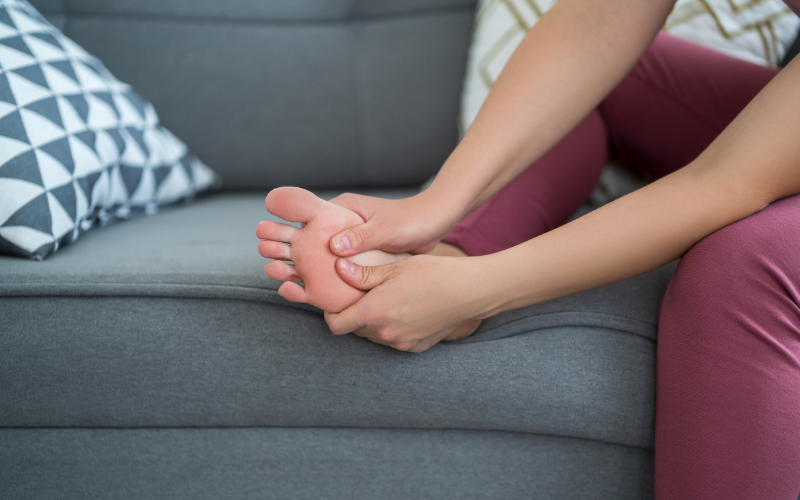

Uric acid is produced during the breakdown of purines, compounds found in certain foods. Normally, uric acid is filtered out by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. However, when the body produces excess uric acid or the kidneys do not process it effectively, it can accumulate and cause gout. While some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gout, daily habits significantly contribute to the onset and recurrence of this painful condition.
The Role of Diet in Gout Flare-ups
Diet is one of the most influential daily habits in managing gout. Certain foods can trigger or worsen gout attacks by increasing uric acid levels in the body. High-purine foods, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood like sardines and shellfish, are known to contribute to uric acid buildup. Alcohol, especially beer, is another common culprit, as it inhibits uric acid elimination from the body.
Foods to Avoid for Gout:
- Red meats: Beef, lamb, and pork contain high levels of purines that can increase uric acid production.
- Seafood: Fish like anchovies, sardines, and herring are rich in purines.
- Alcohol: Beer and wine can both elevate uric acid levels and hinder its excretion.
- Sugary drinks: Sodas and other sugary beverages contribute to obesity and can increase uric acid levels.
On the flip side, consuming certain foods can help manage gout. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers, can lower uric acid levels. Low-fat dairy products, cherries, and coffee have also been shown to reduce the risk of gout attacks. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can help flush out uric acid from the body, preventing its buildup.
The Impact of Obesity on Gout
Obesity is closely linked to gout. Excess weight puts added pressure on the joints, increasing the likelihood of joint damage and making gout attacks more frequent. Furthermore, obesity contributes to higher levels of uric acid in the blood. Fat cells produce substances that can interfere with the kidneys’ ability to eliminate uric acid, exacerbating the condition.
How to Manage Weight and Gout:
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help control weight and improve overall health. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are gentle on the joints and effective in managing gout.
- Adopt a balanced diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in purines and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help with weight management.
- Lose weight gradually: Rapid weight loss can lead to an increase in uric acid levels, so aim for a steady and sustainable weight loss of 1–2 pounds per week.
By maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can reduce the pressure on their joints and lower the risk of gout flare-ups. Weight loss can also improve the body’s ability to process uric acid and prevent its accumulation in the joints.
The Importance of Hydration for Gout Management
Dehydration is another common factor that can trigger gout attacks. When the body is dehydrated, it is less able to excrete uric acid, leading to a higher concentration in the blood. This can result in the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints, causing pain and inflammation.
To prevent gout attacks, it is important to stay hydrated throughout the day. Aim to drink at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water daily, or more if you’re active or live in a hot climate. Staying hydrated helps the kidneys flush out excess uric acid, reducing the risk of crystal formation.
Tips for Staying Hydrated:
- Drink water regularly: Carry a water bottle and sip throughout the day.
- Limit sugary drinks: Avoid sodas and sugary beverages, which can increase uric acid levels.
- Eat hydrating foods: Incorporate water-rich foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges into your diet.
In addition to preventing gout, staying hydrated has other health benefits, such as supporting kidney function and improving overall joint health.
The Effect of Physical Activity on Gout
While intense physical activity or injury can trigger a gout flare-up, regular moderate exercise is beneficial for gout management. Physical activity helps reduce body weight, lower inflammation, and improve circulation. Exercise also strengthens muscles around the joints, providing support and reducing strain on the affected areas.
However, it’s important to avoid overexertion or high-impact activities that can exacerbate joint pain. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent choices for individuals with gout.
How to Exercise Safely with Gout:
- Start slowly: If you’re new to exercise, begin with light activities and gradually increase intensity.
- Focus on low-impact exercises: Swimming and biking are great for joint health and can help you stay active without putting stress on the joints.
- Rest during flare-ups: If you’re experiencing a gout attack, rest and allow the affected joint time to heal before returning to physical activity.
By incorporating regular, low-impact exercise into your daily routine, you can manage your weight, reduce inflammation, and improve joint flexibility, all of which help reduce the frequency of gout flare-ups.
The Impact of Sleep and Stress on Gout
Both sleep and stress play a significant role in gout management. Chronic stress can increase uric acid levels in the blood and lead to flare-ups. It also promotes inflammation, which worsens the symptoms of gout. On the other hand, quality sleep helps the body recover, reduces stress, and supports the immune system.
Tips for Better Sleep and Stress Management:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
- Establish a regular sleep routine: Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep each night to allow your body to rest and recover.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: Both substances can interfere with sleep patterns and exacerbate gout symptoms.
By managing stress and prioritizing good sleep hygiene, you can reduce inflammation and improve your overall health, ultimately reducing the risk of gout flare-ups.
Conclusion
Gout is a complex condition influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics and daily habits. By making changes to your diet, exercise routine, hydration levels, and stress management techniques, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. While medical treatments are essential in managing gout, adopting healthy daily habits is key to preventing flare-ups and improving joint health. By understanding the connection between gout and daily habits, you can take control of your health and lead a life free from the pain and discomfort of gout.
Leave a Reply