Gout is a painful and complex form of arthritis that has been affecting people for centuries. It occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, often leading to sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling. Commonly affecting the big toe, gout can also target other joints, causing discomfort and immobility. While the condition is chronic, modern treatment options provide effective ways to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Let’s delve into the causes, symptoms, and contemporary methods for managing gout effectively.
What Causes Gout?
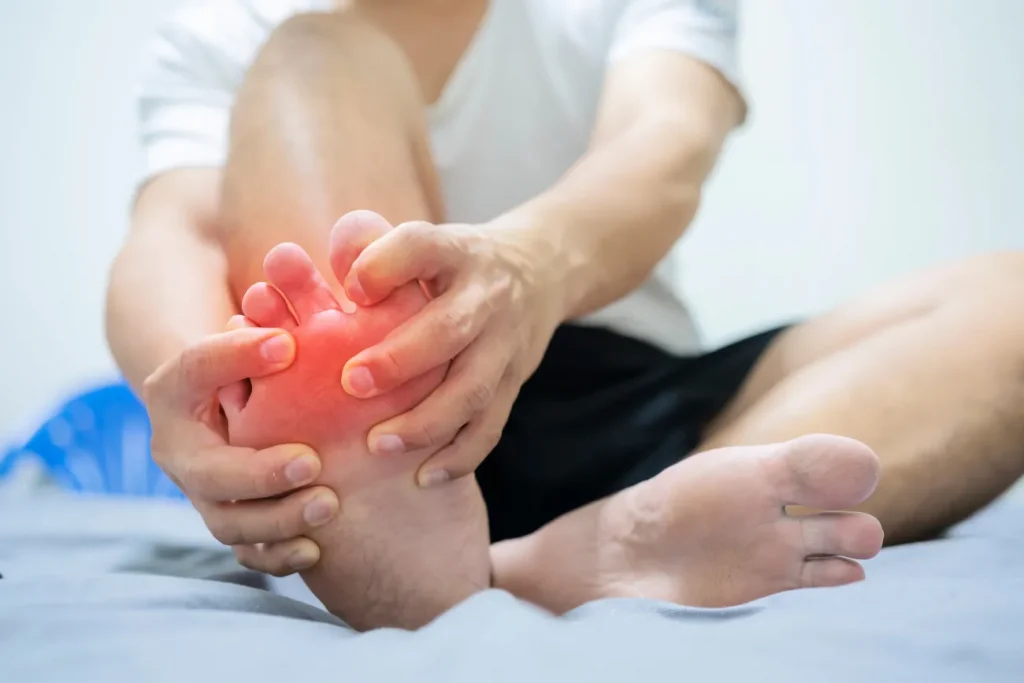
Gout results from hyperuricemia, a condition where excessive uric acid accumulates in the blood. This buildup can stem from several factors, including:
- Dietary Habits: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood, can elevate uric acid levels.
- Alcohol Intake: Drinks like beer and spirits hinder the elimination of uric acid from the body.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of developing hyperuricemia.
- Genetics: A family history of gout can predispose individuals to the condition.
- Medical Conditions: Kidney disease, hypertension, and diabetes can contribute to uric acid buildup.
- Medications: Diuretics and certain drugs used to manage high blood pressure may elevate uric acid levels.
Recognizing Gout Symptoms
Gout typically manifests in four stages, each with distinct symptoms:
- Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia: High uric acid levels without noticeable symptoms.
- Acute Gout Attack: Sudden, intense joint pain accompanied by redness, swelling, and warmth. These attacks often occur at night and can last several days.
- Intercritical Gout: A symptom-free period between acute attacks. Without treatment, another flare-up may occur.
- Chronic Tophaceous Gout: Long-term gout can lead to permanent joint damage, with tophi—lumps of uric acid crystals—forming under the skin.
Modern Treatment Methods for Gout
Managing gout involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments. Here are the most effective methods:
1. Medications for Gout Management
Pharmaceutical treatments play a vital role in reducing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Common medications include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during an attack.
- Colchicine: This anti-inflammatory drug is particularly effective during acute gout flare-ups.
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone and other steroids help reduce inflammation and pain, especially when NSAIDs are not suitable.
- Urate-Lowering Therapies: Medications like allopurinol and febuxostat reduce uric acid production, preventing future attacks.
- Uricosuric Agents: Probenecid helps the kidneys remove excess uric acid from the body.
2. Dietary Adjustments
A gout-friendly diet focuses on reducing purine intake and maintaining healthy uric acid levels. Key dietary tips include:
- Limit High-Purine Foods: Avoid organ meats, shellfish, and certain types of fish like anchovies and sardines.
- Increase Low-Purine Foods: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products into your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out uric acid and reduces the risk of crystal formation.
- Reduce Alcohol and Sugary Drinks: Limiting these beverages can prevent uric acid spikes.
3. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing gout risk. Excess body fat contributes to higher uric acid levels, so adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise can aid in weight control and overall health improvement.
4. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through alternative treatments, including:
- Herbal Remedies: Cherries, ginger, and turmeric are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce gout symptoms.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may alleviate joint pain and promote healing.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening and improving joint mobility can help reduce the severity of symptoms.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in managing gout:
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking improve joint health and overall well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep supports the body’s healing process and reduces stress, which can trigger gout attacks.
- Stress Management: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help lower stress levels and minimize the risk of flare-ups.
Preventing Gout Flare-Ups
Prevention is a crucial aspect of gout management. Here are some effective strategies to avoid flare-ups:
- Monitor Uric Acid Levels: Regular blood tests can help track uric acid levels and detect potential risks early.
- Adhere to Medication Plans: Consistently taking prescribed medications can prevent uric acid buildup and reduce the frequency of attacks.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Stick to a low-purine, nutrient-rich diet to keep gout symptoms under control.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity promotes overall health and reduces the likelihood of gout episodes.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and steer clear of foods, drinks, and lifestyle habits that provoke symptoms.
Gout and Long-Term Health
Untreated gout can lead to serious complications, including chronic joint damage, kidney stones, and cardiovascular issues. Therefore, it is essential to address symptoms promptly and adopt a comprehensive treatment plan. By combining medical treatments with lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Technology in Gout Management
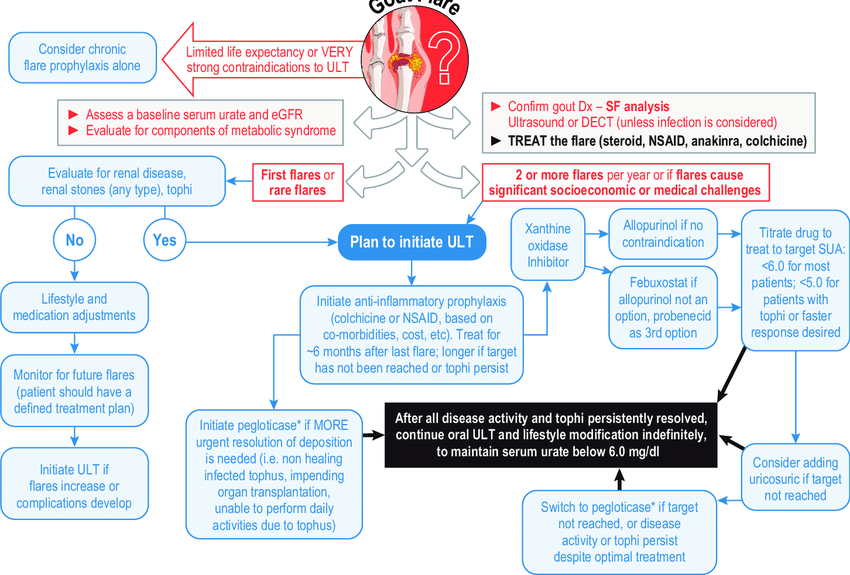
Advancements in technology have made gout management more accessible. Mobile apps now allow individuals to track uric acid levels, log dietary habits, and receive reminders for medication. Telemedicine also enables patients to consult with healthcare professionals without visiting a clinic, ensuring timely and convenient care.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Gout
Gout, though painful and disruptive, can be managed effectively with the right combination of treatments and lifestyle changes. From medication to dietary adjustments and alternative therapies, numerous options are available to alleviate symptoms and prevent future attacks. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can lead healthier, more comfortable lives free from the debilitating effects of gout.

Leave a Reply