In the world of business finance, both management accounting and financial statements play vital roles in ensuring an organization’s success. While financial statements provide an overview of a company’s financial performance, management accounting offers a deeper insight into how internal decision-making and strategy can influence those results. Understanding the connection between these two areas is crucial for business owners, managers, and stakeholders who are looking to optimize their operations and achieve long-term financial health. This article will explore the relationship between management accounting and financial statements, highlighting their practical applications and the benefits they bring to business management.
What is Management Accounting?
Management accounting involves the process of preparing, analyzing, and using financial data to make informed business decisions. Unlike financial accounting, which focuses on the preparation of external reports for stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and regulators, management accounting provides internal reports designed to help managers make day-to-day operational decisions. These reports include budget forecasts, cost analysis, and performance assessments, helping managers optimize resources and achieve business objectives.
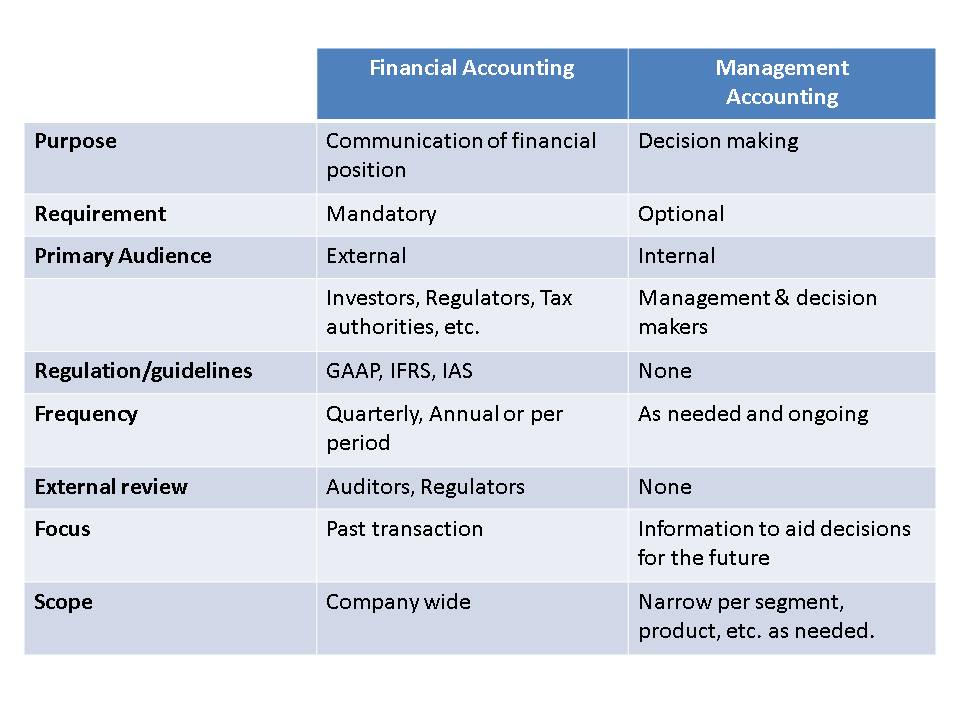
The primary goal of management accounting is to support managerial decision-making by providing relevant and timely financial information. By using this information, managers can evaluate business performance, control costs, assess profitability, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and efficiency.
Key Elements of Management Accounting
Management accounting covers several key areas, including:
- Cost Accounting: This involves tracking, recording, and analyzing costs associated with producing goods or services. Cost accounting helps businesses identify inefficiencies, manage expenditures, and improve profitability.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Management accountants create budgets and forecasts to predict future financial outcomes. These projections help companies plan for potential expenses, investments, and revenue targets.
- Financial Performance Analysis: By comparing actual performance to budgeted figures, management accountants identify areas where the business is excelling or falling short. This analysis enables corrective actions to be taken swiftly.
- Decision Support: Management accounting provides the necessary data for making informed decisions, such as pricing strategies, product line decisions, or capital expenditures.
The Role of Financial Statements
Financial statements are formal records that summarize a company’s financial activities and provide an overview of its financial position. These documents are essential for external stakeholders to assess the financial health of a business. The primary financial statements include:
- Balance Sheet: This statement provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It helps assess the company’s financial stability and liquidity.
- Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement): The income statement reports a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a given period. It helps evaluate the company’s profitability and operating efficiency.
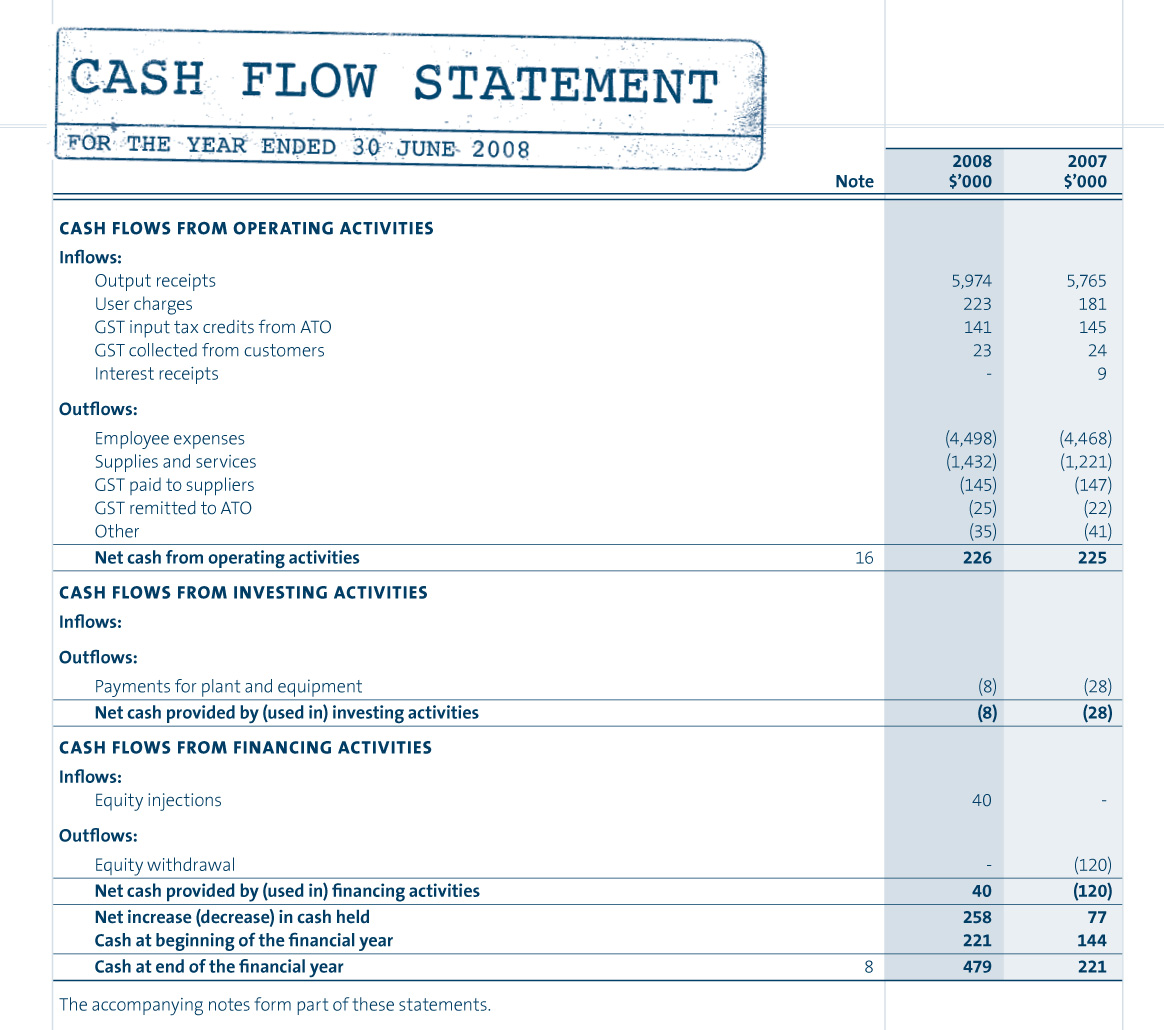
- Cash Flow Statement: This statement outlines the inflows and outflows of cash during a specific period. It helps assess the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations and manage cash resources effectively.
- Statement of Changes in Equity: This report shows the changes in a company’s equity, reflecting activities such as profit or loss, dividend payments, and share issuance or repurchase.
How Management Accounting and Financial Statements Are Connected
Although management accounting and financial statements serve different purposes, they are deeply interconnected. Financial statements provide a historical view of a company’s financial performance, while management accounting focuses on using that information to make future-oriented decisions. Here’s how they are connected:
1. Using Financial Statements for Decision Making
Management accountants use financial statements to inform decision-making. For example, the balance sheet reveals the company’s assets and liabilities, which management can analyze to make decisions about investments, financing, and operations. The income statement, on the other hand, provides insights into profitability, helping managers assess which areas of the business are performing well and which need improvement.
By analyzing the data in financial statements, management accountants can identify trends, project future performance, and recommend strategies for improvement.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting with Financial Data
Financial statements serve as the foundation for budgeting and forecasting in management accounting. Historical data from the income statement and balance sheet are used to create budgets and forecasts that project future revenues, expenses, and profits. By comparing actual financial results with budgeted figures, management can assess the accuracy of their projections and adjust strategies as needed.
3. Cost Management and Profitability Analysis
Cost accounting, a key component of management accounting, is informed by financial statements. For example, the income statement reveals a company’s total expenses, allowing managers to analyze cost structures and identify areas where expenses can be reduced or optimized. Similarly, the balance sheet shows the company’s investments in assets, which can be analyzed to ensure that resources are being used efficiently to generate returns.
4. Cash Flow Management
Cash flow is a crucial element of both financial statements and management accounting. The cash flow statement provides insights into how money is flowing in and out of the business. Management accountants use this information to monitor cash availability, manage liquidity, and make decisions regarding financing, investments, and operational expenditures.
By analyzing cash flow patterns, management can anticipate cash shortfalls and take proactive measures to avoid liquidity issues, such as securing short-term financing or delaying discretionary spending.
Practical Applications of Management Accounting and Financial Statements
The integration of management accounting and financial statements is essential for making data-driven decisions. Below are some practical applications of how businesses use this combination:

1. Performance Evaluation
Management accountants use financial statements to evaluate the performance of different departments, product lines, or business units. By comparing actual results with budgeted figures and previous periods, management can identify areas of strength and weakness. This analysis helps businesses optimize operations, allocate resources effectively, and set performance targets.
2. Pricing Decisions
Financial statements provide essential information for setting prices that ensure profitability. Management accountants analyze cost structures, including direct costs (such as materials and labor) and indirect costs (such as overhead), to determine the minimum price that covers costs and generates a profit. This ensures that the business remains competitive while maintaining profitability.
3. Investment and Capital Budgeting
When considering new investments or capital expenditures, management accountants rely on financial data from the income statement and balance sheet to assess the potential return on investment (ROI). Financial statements provide information about the company’s ability to generate profits and manage debt, helping management decide whether to proceed with investments such as acquiring new equipment, expanding operations, or entering new markets.
4. Risk Management
Financial statements are a key tool in identifying financial risks. For example, a company’s balance sheet may reveal high levels of debt, which could increase the risk of default or financial distress. Management accountants use this information to develop risk management strategies, such as reducing debt levels, improving cash flow, or diversifying investments, to ensure long-term stability.
5. Strategic Planning
By combining financial statement analysis with management accounting techniques, businesses can create effective long-term strategic plans. Financial data provides insights into the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, allowing management to make informed decisions about the future direction of the business.
Conclusion
Management accounting and financial statements are interconnected and essential for business success. Financial statements provide valuable historical data, while management accounting uses this information to make informed decisions that drive business growth and profitability. By leveraging both tools, businesses can optimize their operations, improve cash flow, manage costs, and make data-driven strategic decisions. Understanding the connection between these two areas is crucial for any business owner or manager who wants to ensure financial health and long-term sustainability.
Leave a Reply