In the global economy, the need for standardized financial reporting has become more important than ever. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have emerged as the cornerstone of this global effort, aiming to create consistency and transparency in financial statements across borders. IFRS ensures that companies provide relevant, reliable, and comparable financial information that investors, regulators, and other stakeholders can trust. Over time, IFRS has evolved to address new financial complexities, and companies must stay updated with these changes to remain compliant. This article explores how IFRS impacts the preparation of financial statements, the major changes that have occurred over the years, and what companies need to do to adapt.
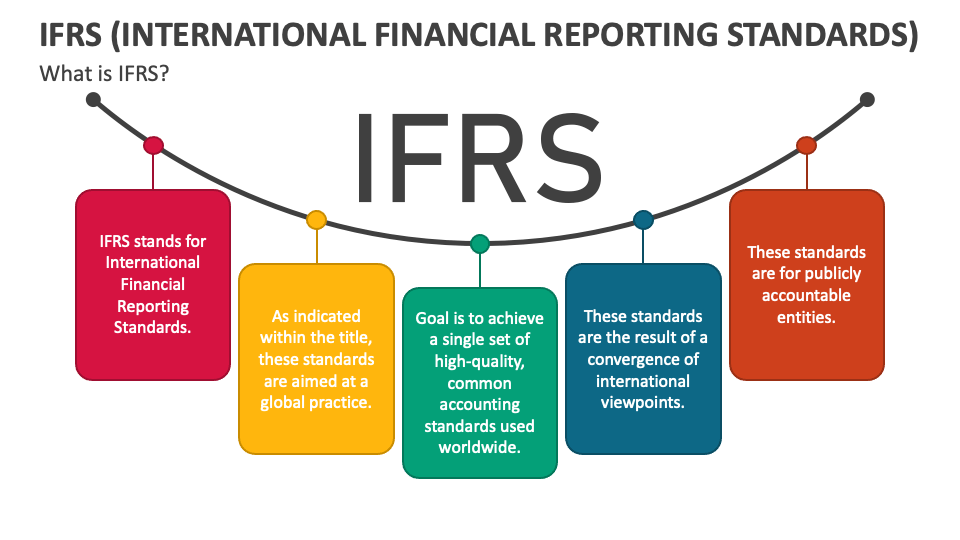
What is IFRS?
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are a set of accounting standards developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). These standards guide companies in preparing and presenting their financial statements in a consistent and transparent manner, ensuring comparability across different industries and countries. IFRS is used in more than 140 countries worldwide, including the European Union, Australia, and parts of Asia, though some countries, such as the United States, use their own Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).

The Importance of IFRS in Financial Reporting
IFRS provides a unified framework that enhances the reliability of financial reporting by offering guidelines on how to recognize, measure, present, and disclose transactions and events in financial statements. This consistency helps investors and financial analysts compare companies more effectively, even across borders. Additionally, IFRS enhances transparency, reduces the risk of manipulation, and promotes trust in financial markets.
Key Changes in IFRS Over the Years
The landscape of financial reporting has evolved significantly with the introduction of IFRS, and several key changes have shaped the way financial statements are prepared. These changes were designed to improve clarity, consistency, and the accuracy of financial reporting.
1. IFRS 15 – Revenue from Contracts with Customers
Introduced in 2018, IFRS 15 significantly altered how companies recognize revenue. The new standard provides a single, comprehensive framework for revenue recognition, replacing various older standards and interpretations. Under IFRS 15, revenue is recognized when control of the goods or services is transferred to the customer, rather than when risks and rewards are transferred, as per previous standards.
Key Impacts:
- Companies must use a five-step model to recognize revenue, including identifying contracts, performance obligations, and transaction prices.
- The new model improves consistency and comparability of revenue recognition across industries.
This change required companies to adopt new accounting systems and processes, particularly for industries that had complex or long-term contracts.
2. IFRS 16 – Leases
Another landmark change was the introduction of IFRS 16, which replaced IAS 17 and changed the way leases are reported on the balance sheet. Under the previous standard, operating leases were not recognized on the balance sheet, leading to potential underreporting of liabilities. IFRS 16 requires lessees to recognize most leases on the balance sheet, which affects both the income statement and the financial position of a company.
Key Impacts:
- Lessees must recognize a right-of-use asset and a corresponding lease liability for almost all leases.
- The change significantly affects industries with large lease portfolios, such as retail and aviation.
This change aimed to improve transparency and provide a clearer view of a company’s obligations and assets, thus enhancing financial statement comparability.
3. IFRS 9 – Financial Instruments
IFRS 9, which replaced IAS 39, brought significant changes to the accounting for financial instruments, focusing on classification, measurement, impairment, and hedge accounting. The introduction of this standard marked a shift towards more forward-looking and realistic approaches to accounting for financial assets and liabilities.
Key Impacts:
- Financial assets are classified based on the business model for managing them and their contractual cash flow characteristics.
- The introduction of a new impairment model requires companies to recognize expected credit losses, making the process more proactive rather than reactive.
The application of IFRS 9 has been particularly impactful for financial institutions and companies dealing with large amounts of financial instruments.
4. IFRS 17 – Insurance Contracts
The introduction of IFRS 17 in 2021 replaced IFRS 4 and represented a fundamental overhaul of insurance accounting. This standard aims to increase transparency in the insurance industry by providing a more consistent approach to the recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of insurance contracts.
Key Impacts:
- Insurers must measure insurance contracts using a current estimate of future cash flows, with a risk adjustment and a contractual service margin.
- The standard introduces more detailed disclosures and emphasizes the importance of providing relevant information to users of financial statements.
IFRS 17 is expected to improve comparability and consistency within the insurance sector, particularly for international investors.
The Benefits of Adapting IFRS
The transition to IFRS offers numerous advantages for companies, especially those with international operations or investors. These benefits include:
1. Enhanced Comparability
IFRS improves the comparability of financial statements, making it easier for investors and analysts to compare companies from different regions. With standardized reporting, businesses can highlight their performance and financial position in a way that is consistent with global practices.
2. Improved Transparency
By adhering to IFRS, companies enhance transparency in their financial reporting. IFRS encourages detailed disclosures that provide stakeholders with a deeper understanding of a company’s financial health, risks, and performance. This helps foster trust and confidence among investors, regulators, and creditors.
3. Greater Investor Confidence
Investors are more likely to trust companies that follow internationally recognized accounting standards. When a company adheres to IFRS, it assures investors that its financial statements reflect an accurate and fair view of the company’s financial position and performance. This can lead to more investment opportunities and better access to capital.
4. Easier Cross-Border Business
For companies operating across borders, using IFRS ensures consistency in financial reporting, facilitating smoother mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships. Companies that adopt IFRS can more easily engage with international stakeholders and expand their market reach.
The Challenges of Adopting IFRS
While the benefits of IFRS are numerous, the transition to these international standards can be challenging. Some of the key challenges companies face include:
1. Complexity of Implementation
Adopting IFRS often requires significant changes in accounting systems, processes, and staff training. Businesses may need to invest in new software, hire additional personnel with expertise in IFRS, and ensure that their financial reporting practices are aligned with the new standards.
2. Cost of Compliance
The cost of implementing IFRS can be substantial, especially for smaller companies with limited resources. This includes the costs of training, system upgrades, and additional audits. However, many businesses view these costs as a long-term investment in transparency and comparability.
3. Continuous Updates and Adaptation
IFRS is constantly evolving to address new financial reporting challenges. Companies must stay updated on changes and ensure they adapt their financial reporting practices accordingly. Failure to do so may result in non-compliance, which can have significant legal and financial consequences.
How to Adapt to IFRS
To ensure successful adoption of IFRS, companies should consider the following steps:

1. Develop a Comprehensive Transition Plan
A detailed plan is essential for successfully implementing IFRS. This plan should include a timeline, resource allocation, and a strategy for addressing the specific changes in each standard that affects the company’s operations.
2. Invest in Training and Resources
It is crucial to ensure that finance teams and accounting professionals are well-versed in IFRS. This can be achieved through training, attending workshops, or hiring experts with experience in IFRS.
3. Leverage Technology
Adopting IFRS may require updates to financial software and reporting systems. Companies should invest in technology that supports IFRS-compliant accounting practices, ensuring that the transition is smooth and efficient.
4. Consult with External Experts
Many companies benefit from consulting with external auditors, legal advisors, and IFRS experts to ensure that they are fully compliant with the standards.
Conclusion
The adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) has revolutionized the way companies prepare and present their financial statements. While the transition to IFRS can be complex and costly, the long-term benefits, such as enhanced transparency, comparability, and investor confidence, make it a valuable undertaking for companies with international operations or those seeking to expand globally. By staying up-to-date with the latest IFRS changes and ensuring compliance, companies can ensure that their financial reporting remains reliable, relevant, and trusted by stakeholders around the world.
Leave a Reply