Cancer remains one of the most feared diseases worldwide, with millions of people diagnosed each year. Despite the significant advancements in treatment options, many still wonder: Can cancer be cured? This question is not easily answered, as the response depends on various factors, such as the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient’s overall health. However, experts agree that while a universal cure may not yet exist, many cancers can be treated effectively, and the chances of recovery continue to improve. In this article, we’ll explore the latest insights from oncology specialists, delve into available treatments, and discuss the future of cancer treatment.
Understanding Cancer and the Challenge of Finding a Cure
Cancer is not a single disease but a collection of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth. These rogue cells can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious health complications. The complexity of cancer, its ability to evolve and resist treatment, and its varied manifestations across different body parts contribute to the difficulty of finding a cure.
While early detection and intervention play a crucial role in successful cancer treatment, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Cancers differ in their genetic makeup, progression, and how they respond to treatment. As a result, a treatment or cure that works for one type of cancer may not be as effective for another.
Current State of Cancer Treatment
Currently, cancer treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy. These treatments aim to remove or destroy cancer cells, slow down their growth, or stimulate the immune system to fight the disease. While these therapies have helped millions of cancer patients live longer, healthier lives, they don’t guarantee a cure for everyone.
Surgery
Surgical removal of tumors is one of the most common treatments for localized cancers, such as breast, lung, and colon cancer. When cancer is detected early and is confined to one area, surgery can be a curative option. In cases where cancer has spread, surgery may be used to remove as much of the tumor as possible to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses powerful drugs to kill fast-growing cancer cells throughout the body. It is commonly used for cancers that have spread beyond the original tumor site. While chemotherapy can be effective in shrinking tumors and killing cancer cells, it can also damage healthy cells, leading to side effects like hair loss, nausea, and fatigue.
Chemotherapy is often used in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or radiotherapy, to enhance its effectiveness. However, chemotherapy alone may not always result in a cure, especially in advanced stages of cancer.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy, or radiation therapy, uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It is often used to shrink tumors before surgery or to treat cancer cells that remain after surgery. Like chemotherapy, radiotherapy can cause damage to healthy tissues, leading to side effects. However, for localized cancers, radiotherapy can be highly effective and, in some cases, may lead to remission.
Immunotherapy
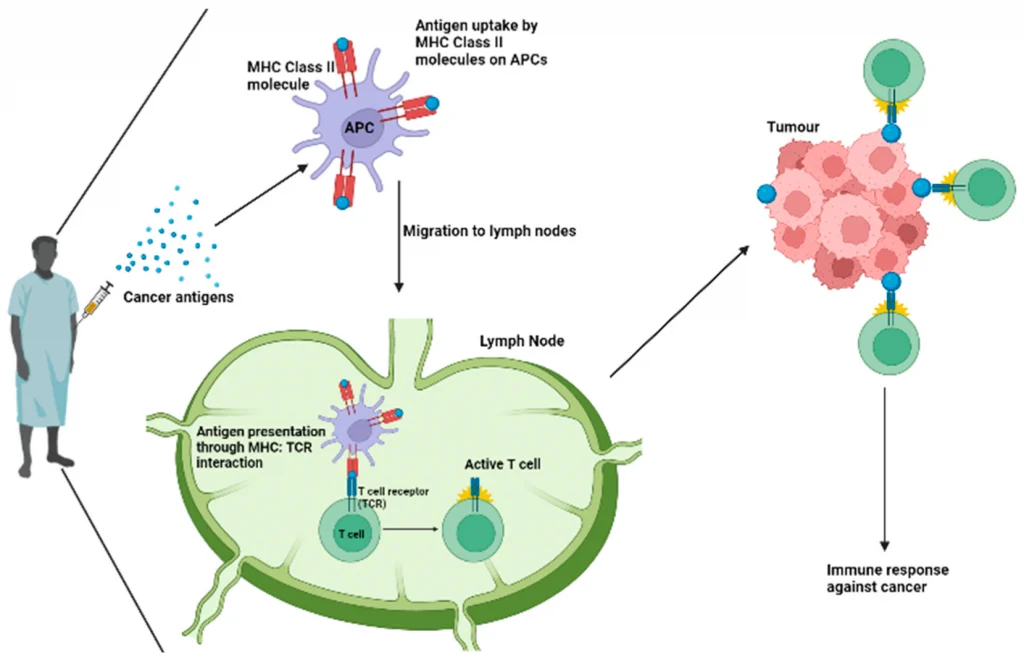
Immunotherapy is a newer form of cancer treatment that boosts the body’s immune system to recognize and fight cancer cells. It has shown promising results in treating cancers that are resistant to traditional therapies, such as melanoma, lung cancer, and certain types of leukemia. Immunotherapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, and while it has led to complete remission in some patients, it is still a relatively new field with ongoing research.
The Role of Early Detection in Cancer Treatment
The earlier cancer is detected, the better the chances of successful treatment. Early-stage cancers are often more localized and easier to treat, making them more likely to be cured. Advances in diagnostic technology, such as imaging techniques, blood tests, and genetic testing, have made it easier for doctors to detect cancer at an earlier stage.
Screening programs for cancers like breast, prostate, and colon cancer have also contributed to the early detection of the disease. These programs help identify high-risk individuals and detect abnormalities before they become symptomatic, allowing for more effective interventions.
Can Cancer Be Cured with Current Treatments?
While a definitive cure for all cancers remains elusive, several types of cancer can be treated effectively, especially if caught early. For example, cancers such as testicular, thyroid, and certain types of skin cancer (e.g., basal cell carcinoma) have high cure rates when detected early and treated appropriately.
In some cases, patients have achieved long-term remission after undergoing aggressive treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation. For others, a combination of therapies may be required to control the disease and extend life. However, even with the latest treatments, some cancers remain resistant to available therapies, and the prognosis may vary significantly between individuals.
Advances in Cancer Research and Potential Cures
The field of cancer research is advancing at a rapid pace. New discoveries are being made every day that could bring us closer to finding a cure for cancer. Some of the most promising areas of research include:
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are drugs designed to target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. These therapies focus on the genetic and molecular factors that drive cancer, allowing for more precise treatment. Targeted therapy has shown success in treating cancers like breast cancer, lung cancer, and leukemia.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy aims to correct genetic mutations that lead to cancer. By modifying or replacing faulty genes, this approach seeks to stop cancer from growing or spreading. While gene therapy is still in the experimental stages, it holds great potential as a future cancer treatment option.
CAR-T Cell Therapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is a revolutionary treatment that modifies a patient’s T cells to better target and destroy cancer cells. CAR-T therapy has already shown remarkable results in treating certain blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. This therapy is still under study for other cancer types, but its success in clinical trials offers hope for the future.
Immunotherapy Advancements
As immunotherapy continues to evolve, researchers are discovering new ways to enhance its effectiveness. Combination therapies that combine immunotherapy with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or targeted therapies are showing promise in improving patient outcomes.
The Importance of Personalized Cancer Treatment
Because cancer is such a complex disease, personalized treatment plans are crucial for achieving the best outcomes. Personalized cancer treatment involves tailoring therapy to the individual’s specific cancer type, genetic profile, and overall health. This approach allows for more precise targeting of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.

Precision medicine, which involves using genetic testing to guide treatment decisions, is already being used in some cancer treatments. As technology advances, personalized treatments are expected to become more common and may lead to better survival rates and, in some cases, a cure.
Can Cancer Be Prevented?
While not all cancers are preventable, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of developing cancer. Smoking cessation, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and limiting alcohol consumption can lower the risk of several cancers, including lung, colorectal, and liver cancer. Additionally, vaccination programs against viruses like HPV and hepatitis B have been shown to reduce the risk of certain cancers, such as cervical and liver cancer.
Conclusion: A Cure for Cancer Is Possible, But Challenges Remain
So, can cancer be cured? The short answer is that while a universal cure for all cancers is still out of reach, significant progress has been made in the treatment and management of the disease. Many types of cancer can be effectively treated, especially when diagnosed early. Advancements in immunotherapy, targeted therapy, gene therapy, and personalized medicine offer hope for more effective treatments and, eventually, cures for certain cancers.
With ongoing research, improved diagnostics, and better treatment options, cancer patients today have more reasons to be hopeful than ever before. While we may not yet have a cure for every form of cancer, the future holds tremendous promise for those battling this disease. The key lies in early detection, personalized care, and continuing advancements in the fight against cancer.

Leave a Reply