Understanding the intricate connection between the brain and mental health has reached unprecedented heights with the merging of neuroscience and psychology. Advances in these fields have transformed the way anxiety and trauma are treated, offering hope to millions. By decoding the neurological underpinnings of these conditions, researchers and clinicians are developing cutting-edge therapies and interventions that are both effective and personalized.
This article delves into the latest breakthroughs, examining how neuroscience informs psychological practices and reshapes the future of mental health care.
The Neurological Basis of Anxiety and Trauma
How the Brain Processes Anxiety
Anxiety stems from overactivity in the brain’s fear-processing regions, particularly the amygdala. This almond-shaped structure signals perceived threats, even when no actual danger exists. Simultaneously, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for regulating emotions and decision-making, often struggles to mitigate this overactivation. Understanding this imbalance has been pivotal in creating treatments that aim to restore equilibrium.

Trauma’s Impact on Brain Function
Trauma leaves a lasting imprint on neural pathways. Chronic stress resulting from traumatic events can enlarge the amygdala, shrink the hippocampus (critical for memory), and weaken the prefrontal cortex. These changes disrupt emotional regulation, memory processing, and the ability to distinguish past trauma from present safety. Neuroscience has illuminated these alterations, paving the way for interventions that promote neural healing.
Cutting-Edge Treatments Inspired by Neuroscience
1. Exposure Therapy Enhanced by Brain Imaging
Exposure therapy, a cornerstone for treating anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), has been revolutionized by neuroimaging tools like functional MRI (fMRI). These technologies allow clinicians to observe brain activity during therapy sessions, tailoring treatments to individual neural responses. This precision improves therapy effectiveness and reduces relapse rates.
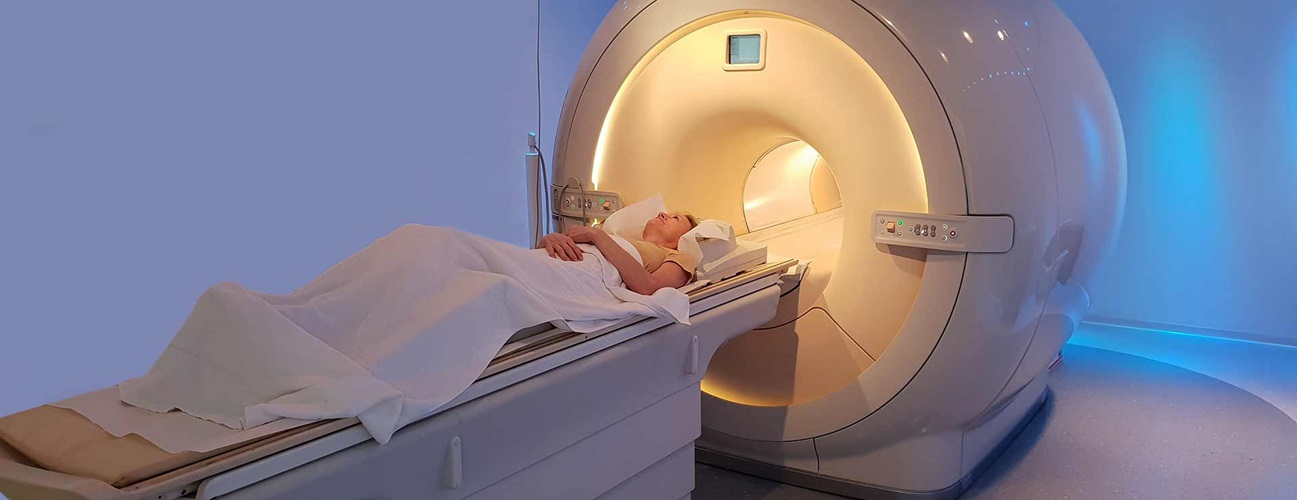
2. Neurofeedback Training
Neurofeedback uses real-time brainwave monitoring to teach patients how to regulate their brain activity. This non-invasive method targets regions associated with anxiety and trauma, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Studies have shown that neurofeedback can significantly reduce symptoms by promoting self-regulation and resilience.
3. Virtual Reality Therapy
Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a powerful tool for immersive exposure therapy. Patients confront anxiety-provoking scenarios in a controlled, simulated environment, allowing them to process fears safely. For trauma survivors, VR offers a means to revisit memories with reduced emotional intensity, facilitating desensitization and emotional integration.
4. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)

TMS delivers magnetic pulses to specific brain regions, modulating neural activity. Approved for treatment-resistant depression, this technique is now being explored for anxiety and PTSD. By targeting areas like the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, TMS can recalibrate overactive circuits, alleviating symptoms without medication.
Bridging Neuroscience and Psychological Therapies
The Role of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
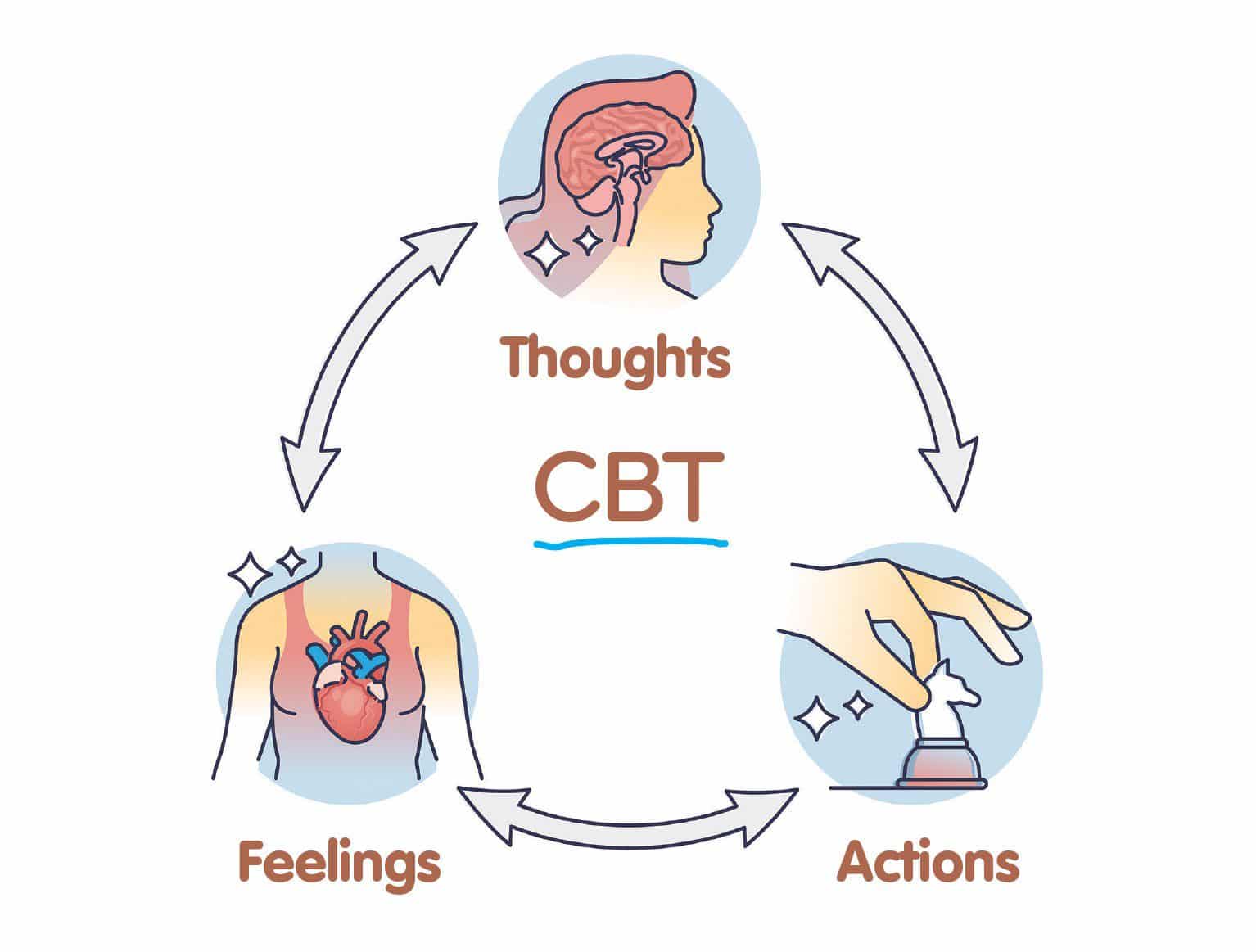
CBT remains a gold standard in treating anxiety and trauma, but its integration with neuroscience has enhanced its impact. Brain imaging studies reveal how CBT reshapes neural networks, strengthening connections in the prefrontal cortex and dampening overactive fear responses in the amygdala. This evidence-based approach reinforces the brain’s ability to unlearn maladaptive thought patterns.
Mindfulness and Brain Health
Mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) leverage the brain’s neuroplasticity to promote healing. Regular mindfulness practice reduces amygdala activation and increases gray matter density in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. These changes support emotional regulation, stress reduction, and recovery from trauma.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR combines psychological principles with neural stimulation to address trauma. By engaging bilateral brain activity through guided eye movements, EMDR helps reprocess traumatic memories. Neuroscience explains its efficacy by showing how this method disrupts overactive fear circuits, creating new associations and reducing distress.
The Promise of Personalized Treatments
Genetics and Individualized Care
Advances in genetics are informing personalized mental health care. Researchers have identified genetic markers that influence susceptibility to anxiety and trauma, as well as responses to treatment. This knowledge allows clinicians to tailor interventions based on an individual’s unique genetic profile, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Biomarker Discovery
Biomarkers, such as cortisol levels and brain imaging patterns, are being used to predict treatment outcomes. These indicators help identify which patients will benefit most from specific therapies, from medication to psychotherapy, reducing trial-and-error approaches.
Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
Recent studies on psychedelics, such as psilocybin and MDMA, highlight their potential in treating trauma-related conditions. By enhancing neural connectivity and reducing fear responses, these substances facilitate deep psychological breakthroughs when paired with therapy. Neuroscience provides the framework for understanding their transformative effects and ensuring safe application.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Accessibility and Equity
While neuroscience-driven therapies show immense promise, their cost and complexity pose barriers to widespread adoption. Ensuring equitable access to these innovations remains a priority for mental health advocates.
Ethical Use of Technology
As treatments like VR and neurofeedback advance, ethical questions about data privacy and patient autonomy arise. Safeguarding sensitive brain data is essential to maintaining trust in these technologies.
Balancing Innovation with Evidence
The rapid pace of innovation necessitates rigorous testing to confirm safety and effectiveness. Striking a balance between adopting novel treatments and relying on proven methods ensures patient safety while fostering progress.
The Future of Anxiety and Trauma Treatment
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/futureofmentalhealthcare-recirc1-971b0c8b24cb4a46a9ef62c83d925be6.jpg)
The convergence of neuroscience and psychology marks a paradigm shift in mental health care. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the potential for even more targeted, effective treatments is immense. Emerging therapies, such as brain-computer interfaces and advanced biomarker analysis, hold promise for revolutionizing how anxiety and trauma are understood and addressed.
As neuroscience continues to illuminate the brain’s complexities, the integration of these insights into therapeutic practices offers hope for millions navigating mental health challenges. This interdisciplinary approach not only improves outcomes but also fosters a deeper understanding of the human experience.
Conclusion
The integration of neuroscience and psychology is transforming anxiety and trauma treatment, offering innovative solutions that address these conditions at their root. From neurofeedback to personalized care, these advancements empower individuals to reclaim their mental well-being. Have you explored any neuroscience-based therapies, or are you curious to learn more? Share your thoughts or connect with our experts to explore cutting-edge resources on our website!

Leave a Reply