Fungal infections are common and often treatable with over-the-counter remedies. However, there are times when these conditions persist or worsen, signaling the need for medical attention. Understanding when to consult a healthcare provider is crucial to prevent complications and ensure effective treatment. Persistent fungal infections can indicate underlying health issues or resistance to standard treatments.
This article will explore the signs that suggest it’s time to see a doctor, what to expect during a medical consultation, and how to manage chronic fungal conditions.
Recognizing Persistent Fungal Infections
Fungal infections occur when fungi grow excessively on the skin, nails, or mucous membranes. They can develop in various areas, including the feet, scalp, nails, and genitals. While these infections are usually mild, chronic cases require more attention.
Signs of Persistent Fungal Infections
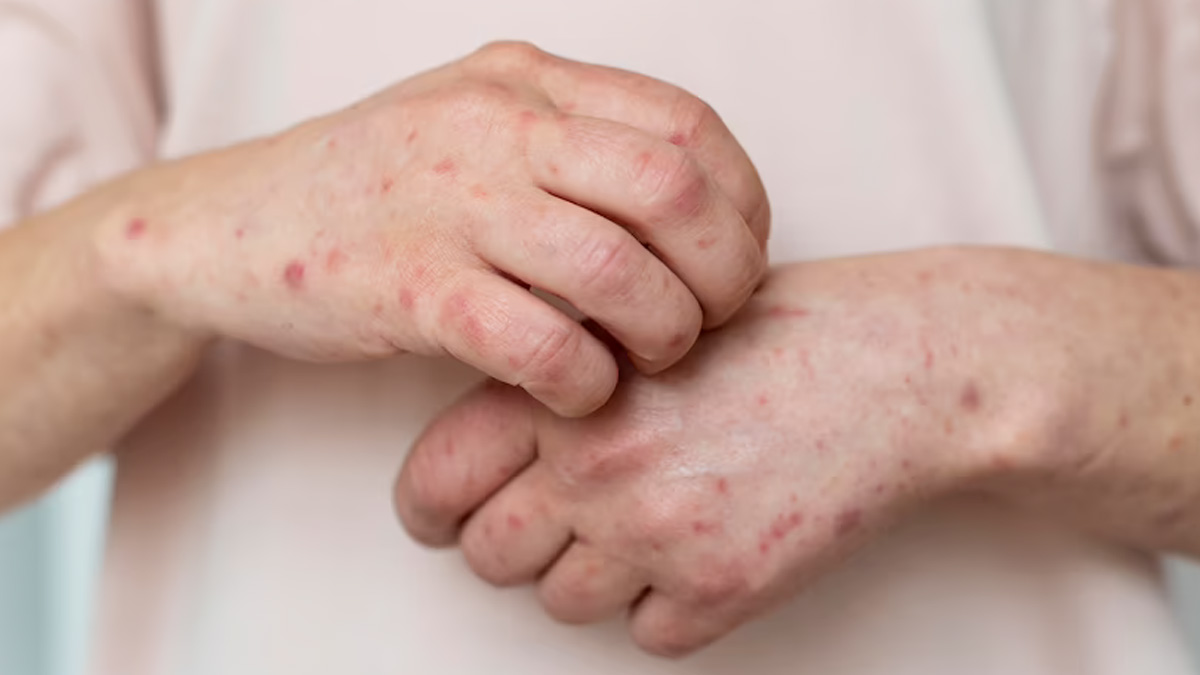
- Prolonged Symptoms: If redness, itching, or scaling persists for more than two weeks despite using antifungal treatments, it’s time to seek help.
- Worsening Condition: Symptoms such as increased pain, swelling, or the spread of the infection to other areas indicate a lack of response to initial remedies.
- Recurrent Infections: Repeated fungal outbreaks in the same location may signify an underlying problem or insufficient treatment.
- Thickened or Discolored Nails: Persistent nail fungus that doesn’t improve with topical treatments may require oral antifungal medication or other interventions.
Risk of Delayed Treatment
Neglecting persistent fungal infections can lead to complications, including:
- Secondary bacterial infections from scratching or broken skin.
- Spreading the infection to other body parts or individuals.
- Permanent nail damage or scarring.
When to Consult a Doctor
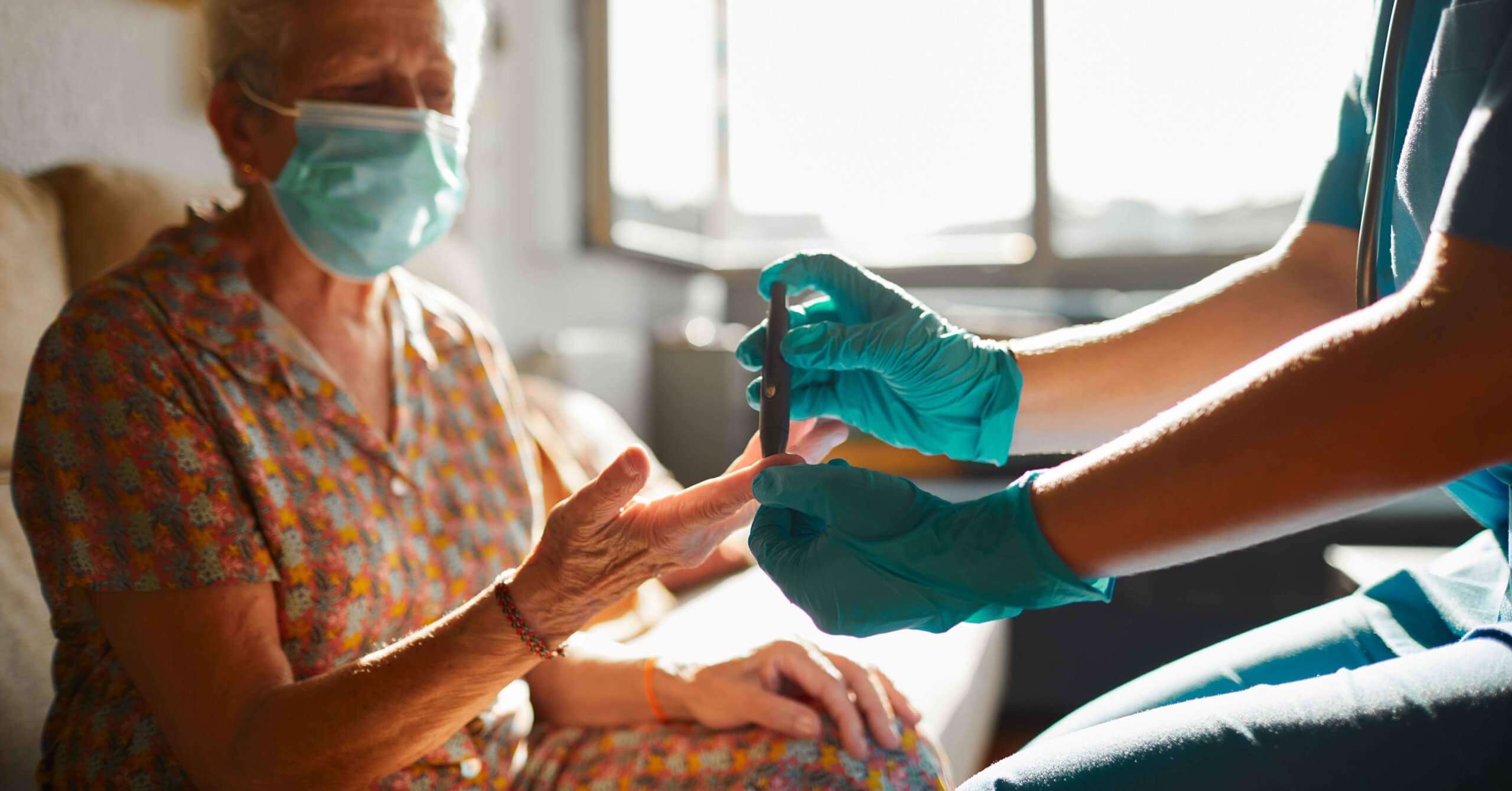
Persistent fungal infections are not only uncomfortable but can also disrupt daily life. Consulting a medical professional ensures that you receive accurate diagnoses and tailored treatments.
1. Symptoms Beyond Mild Discomfort
If itching, burning, or pain interferes with daily activities or sleep, a doctor’s evaluation is essential. Severe symptoms could indicate a deeper fungal infection requiring more potent medications.
2. Ineffectiveness of Over-the-Counter Medications
Most mild fungal infections respond well to topical antifungals available at pharmacies. If these fail to improve the condition, it could indicate a resistant strain or misdiagnosis. A healthcare provider can prescribe stronger treatments or conduct tests to confirm the type of infection.
3. Compromised Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, HIV, or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to persistent fungal infections. Medical intervention can help manage infections effectively while addressing other health concerns.
4. Suspected Deep Fungal Infections
In rare cases, fungal infections can penetrate deeper layers of the skin or spread to internal organs, a condition known as systemic mycosis. Symptoms like fever, fatigue, and organ-specific issues require immediate medical attention.
What to Expect During a Medical Consultation
Visiting a doctor for a fungal infection involves a straightforward process aimed at identifying the root cause and determining the best treatment plan.
1. Thorough Assessment
The doctor will examine the affected area and inquire about your symptoms, lifestyle, and medical history. This helps identify potential triggers, such as exposure to damp environments or contact with infected individuals.
2. Diagnostic Tests

To confirm the type of infection, a doctor may perform:
- Skin or Nail Scraping: Samples are taken and examined under a microscope to identify fungal organisms.
- Cultures: Growing fungi in a lab to determine the exact strain for targeted treatment.
- Blood Tests: Used for systemic infections to detect fungal pathogens in the bloodstream.
3. Treatment Options
Depending on the severity and type of infection, a doctor may recommend:
- Topical Antifungals: Creams, sprays, or ointments for mild infections.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: Pills like fluconazole or terbinafine for more stubborn cases.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Tips to prevent recurrence, such as wearing breathable fabrics and maintaining proper hygiene.
Managing Persistent Fungal Infections
Consistent care and preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of recurrence and ensure effective healing.
1. Follow Prescribed Treatment Plans
It’s essential to complete the full course of prescribed medications, even if symptoms improve before finishing. Premature discontinuation can lead to recurrence or drug resistance.
2. Maintain Optimal Hygiene

- Dry the Affected Area: Fungi thrive in moist environments, so keeping skin and nails dry is crucial.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Towels, socks, and footwear should not be shared to prevent cross-contamination.
- Use Antifungal Products Regularly: Consider powders or sprays for shoes and feet, especially in humid climates.
3. Strengthen Your Immune System
A healthy immune system can fend off infections more effectively. Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management to support overall health.
Preventing Future Fungal Infections
Preventive measures go a long way in protecting against recurrent fungal infections.
1. Choose Appropriate Footwear
Wear breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks to keep feet dry. Avoid walking barefoot in communal areas like locker rooms or pools.
2. Address Underlying Health Issues
Conditions such as diabetes or obesity can increase the risk of fungal infections. Managing these conditions effectively can reduce susceptibility.
3. Practice Regular Skincare
Cleanse and moisturize your skin daily, avoiding products that may irritate or excessively dry out the skin.
4. Monitor High-Risk Areas
Pay attention to areas prone to sweating or friction, such as underarms, groin, and between toes. Applying antifungal powder can help prevent infections in these regions.
Conclusion
Persistent fungal infections can be more than a minor inconvenience; they may signal underlying health concerns or require advanced treatments. Recognizing when to seek medical attention is crucial for timely intervention and long-term relief. By understanding the signs, following prescribed treatments, and adopting preventive measures, you can effectively manage and avoid chronic fungal issues.
Do you have lingering questions about fungal infections or related treatments? Share your thoughts or experiences in the comments below. Visit our website for more informative articles and expert health tips to stay ahead of common infections.
Leave a Reply