Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and while genetics can play a role, lifestyle choices are often the deciding factor in whether or not we develop cancer. Many of us unknowingly engage in daily habits that increase our risk of developing this serious disease. From what we eat to how we move, certain actions and behaviors can elevate the chances of cancer, especially when done consistently over time. In this article, we’ll explore common daily habits that increase your risk of cancer, how these habits affect your body, and practical steps you can take to reduce this risk. By making small changes to your daily routine, you can significantly improve your health and lower your chances of developing cancer.
1. Unhealthy Eating Habits
What we eat on a daily basis has a direct impact on our health. Poor nutrition, particularly a diet high in processed foods, red meats, and sugar, is linked to an increased risk of cancer. Research has shown that diets high in unhealthy fats, refined carbohydrates, and low in fruits and vegetables can lead to the development of several types of cancer, including colorectal, breast, and pancreatic cancer.

Processed meats like sausages, bacon, and hot dogs contain carcinogens, which can damage cells and increase cancer risk. Similarly, consuming high amounts of sugary foods and drinks can lead to obesity, which is a significant risk factor for several types of cancer, such as endometrial, breast, and kidney cancers.
2. Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle is one of the most common daily habits that can increase your risk of cancer. Research indicates that physical inactivity is linked to several cancers, including colon, breast, and endometrial cancers. When you’re not active, your body has difficulty regulating its metabolism and may become more prone to insulin resistance, which can lead to higher levels of inflammation and increase cancer risk.
Exercise, on the other hand, helps regulate body weight, strengthens the immune system, and improves overall metabolic health. Regular physical activity not only reduces the risk of cancer but can also lower the risk of recurrence for cancer survivors.
3. Tobacco Use
Smoking is one of the leading causes of cancer and is responsible for about 30% of cancer deaths globally. Tobacco contains over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are known carcinogens. Smoking damages the DNA in your cells, which increases the risk of lung, throat, mouth, bladder, and kidney cancers.
Even if you do not smoke, exposure to secondhand smoke can also increase your cancer risk. Secondhand smoke contains many of the same harmful chemicals as the smoke inhaled by smokers and can cause lung cancer, particularly in non-smokers who live with smokers.
4. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol in excess has been consistently linked to a higher risk of several cancers, including liver, breast, mouth, throat, and colorectal cancers. Alcohol can act as a carcinogen by metabolizing into acetaldehyde, a substance that can damage DNA and interfere with the body’s ability to repair itself. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to chronic liver disease and inflammation, which further increases cancer risk.
Moderation is key when it comes to alcohol. The American Cancer Society recommends limiting alcohol consumption to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. Reducing alcohol intake can significantly lower the risk of cancer over time.
5. Exposure to Sunlight Without Protection
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major cause of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. UV rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can result in cancer.
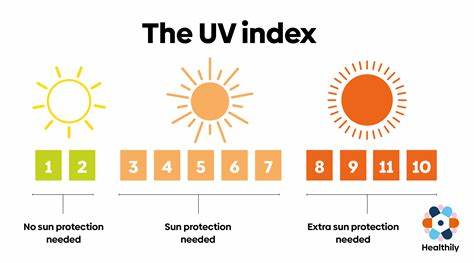
Daily sun exposure without adequate protection, such as sunscreen or protective clothing, significantly increases the risk of skin cancer. Even moderate sun exposure over time can add up and damage the skin. It is important to protect your skin by using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sunlight hours.
6. Chronic Stress and Poor Mental Health
While the connection between mental health and cancer is still being studied, there is evidence to suggest that chronic stress can impact your immune system and increase the risk of developing cancer. Prolonged stress causes the body to produce high levels of cortisol, a hormone that can weaken the immune system and promote inflammation. This creates an environment that may allow cancer cells to grow and spread.
Additionally, people who are stressed are less likely to engage in healthy lifestyle choices such as regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep, which further increases cancer risk. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through mindfulness, yoga, or other relaxation techniques, can help reduce the potential for cancer development.
7. Lack of Sleep and Poor Sleep Hygiene
Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of several health issues, including cancer. Poor sleep habits, such as inconsistent sleep patterns and inadequate sleep duration, can affect the body’s production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep and has been shown to have anti-cancer properties. Studies have suggested that people who work night shifts or have irregular sleep patterns may be at an increased risk for cancers such as breast and prostate cancer.
Prioritizing good sleep hygiene and aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night can help reduce your cancer risk and improve overall health. Creating a consistent bedtime routine and minimizing exposure to screens before sleep can enhance the quality of your rest.
8. Ignoring Preventive Health Screenings
Skipping regular health check-ups and cancer screenings is another common habit that can increase your risk of cancer. Early detection of cancer greatly improves the chances of successful treatment. Many cancers, including breast, colorectal, and cervical cancers, are easier to treat when detected early, before symptoms appear.
Regular screenings, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap smears, can help detect cancer at an early stage when treatment is most effective. Neglecting these screenings, or delaying them, can result in late-stage diagnoses that are harder to treat.
9. Exposure to Environmental Carcinogens
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as air pollution, pesticides, and chemicals in cleaning products, can increase the risk of various cancers. For example, long-term exposure to asbestos is linked to lung cancer and mesothelioma, while certain chemicals in industrial settings can increase the risk of bladder cancer.
To reduce exposure to environmental carcinogens, limit your use of chemical-laden products, and ensure proper ventilation in spaces where you may encounter toxic substances. Being mindful of pollution levels in your area and reducing the amount of time you spend in high-risk environments can also help protect your health.
10. Overuse of Antibiotics and Medications
While medications and antibiotics are necessary for treating infections and various health conditions, overusing them can lead to unintended health consequences. Antibiotic resistance, for example, can make infections harder to treat, while some medications can alter the balance of gut bacteria, leading to inflammation and potentially increasing the risk of certain cancers.

It is important to only use antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional and to follow the prescribed dosage and treatment duration. Avoid self-medicating or overusing medications, as this can affect your body’s overall health and immune function.
Conclusion
Many daily habits, some of which may seem harmless at first, can increase the risk of developing cancer. From poor dietary choices to lack of physical activity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to harmful substances, our lifestyle decisions play a significant role in determining cancer risk. By making small changes to these habits, such as eating a healthy diet, staying active, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, protecting your skin, managing stress, and attending regular screenings, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing cancer and improve your overall quality of life. Taking action today can help safeguard your health for the future.

Leave a Reply