Fungal skin conditions are among the most common dermatological issues people face worldwide. Caused by various types of fungi, these infections often thrive in warm, moist environments, making certain body areas particularly vulnerable. Conditions such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and jock itch can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life if left untreated. Fortunately, they are manageable and often preventable with proper care and knowledge.
This guide explores the most prevalent fungal skin infections, their symptoms, and effective treatment options to help you take control of your skin health.
Understanding Fungal Skin Conditions
Fungal infections affect the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. They are typically superficial but can become severe in immunocompromised individuals. Below, we break down some of the most common types:
1. Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
/assets/production/practices/317736e8895e930e15e7330761f06d2f084c256f/images/2510944.jpg)
Athlete’s foot primarily targets the feet, particularly the areas between the toes. It’s characterized by:
- Symptoms: Itching, burning, redness, peeling, and cracking skin.
- Causes: Fungi that thrive in damp environments like locker rooms, swimming pools, and communal showers.
2. Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
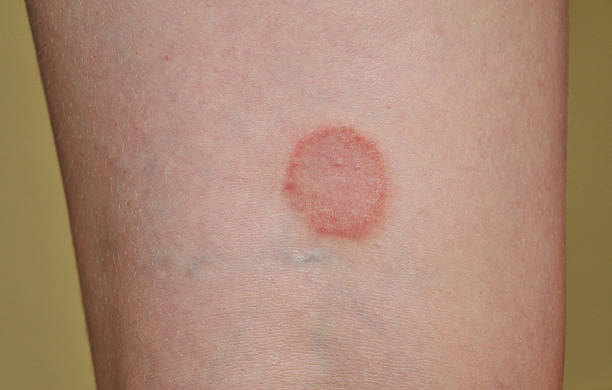
Despite its name, ringworm isn’t caused by worms. Instead, it’s a fungal infection that appears as a circular rash with a clear center.
- Symptoms: Red, scaly patches with a raised border, often itchy.
- Causes: Skin-to-skin contact or contaminated objects like towels and clothing.
3. Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
This infection develops in warm, moist areas, especially the groin and inner thighs.
- Symptoms: Redness, itching, and flaking in the affected area.
- Causes: Excessive sweating, tight clothing, and poor hygiene.
Scalp infections are more common in children but can affect people of all ages.
- Symptoms: Bald patches, scaling, and severe itching.
- Causes: Direct contact with infected individuals, animals, or objects.
5. Candidiasis (Yeast Infections)
Caused by the Candida species, candidiasis affects the skin and mucous membranes.
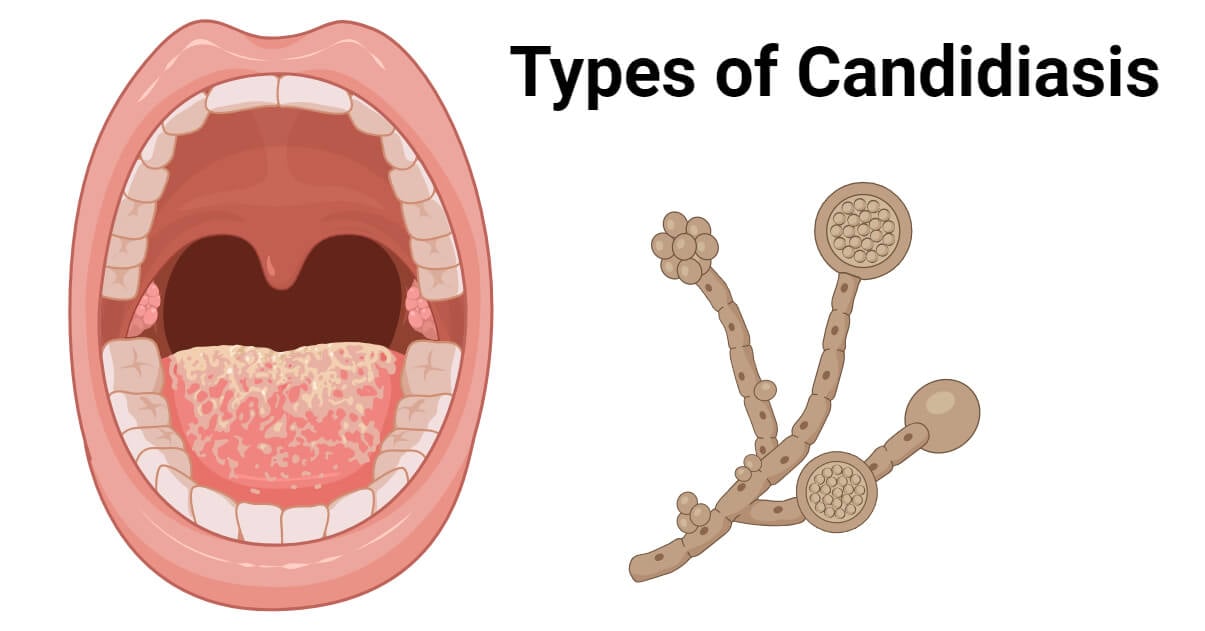
- Symptoms: Red, swollen skin with possible oozing or crusting.
- Causes: Imbalance of natural fungi due to antibiotics, diabetes, or a weakened immune system.
How to Treat Fungal Skin Conditions
Effective treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. Mild to moderate cases can often be managed with over-the-counter remedies, while more persistent infections may require prescription treatments.
1. Over-the-Counter Medications
- Antifungal Creams and Ointments: Products containing clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine work well for athlete’s foot, ringworm, and jock itch.
- Medicated Powders and Sprays: Ideal for keeping areas dry and delivering antifungal agents.
- Shampoos: For scalp infections, shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide are effective.
2. Prescription Treatments
- Topical Medications: Stronger creams or gels for stubborn infections.
- Oral Antifungals: Tablets like terbinafine or itraconazole may be needed for nail or severe skin infections.
3. Natural Remedies

While not a replacement for medical treatment, natural options like tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, or coconut oil can provide relief for mild cases.
4. Hygiene Practices
- Keep affected areas clean and dry.
- Avoid scratching to prevent spreading the infection.
- Wash bedding, towels, and clothing frequently.
Preventing Fungal Infections
Prevention is key to avoiding the discomfort and inconvenience of fungal skin conditions. Here are some practical strategies:
1. Maintain Proper Hygiene
- Shower regularly, especially after sweating.
- Dry skin thoroughly, paying attention to areas prone to moisture.
2. Use Protective Measures
- Wear flip-flops in communal showers and pool areas.
- Choose breathable fabrics to reduce sweating and irritation.
3. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
Fungi can spread through shared objects like towels, socks, and razors. Stick to using your own belongings.
4. Strengthen Your Immune System
A healthy immune system can fight off infections. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and manage stress to support your body’s defenses.
When to See a Doctor
Although most fungal skin infections respond well to over-the-counter treatments, some cases require medical intervention. Seek professional help if:
- Symptoms worsen or persist after two weeks of self-treatment.
- The infection spreads to other areas of the body.
- You have a weakened immune system or underlying medical conditions.
Conclusion
Fungal skin conditions like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and jock itch are common but manageable issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers you to take action and maintain healthy skin. Regular hygiene, the right antifungal products, and preventive habits can make a significant difference in avoiding these infections.
Have you dealt with a fungal skin condition? Share your experiences or tips in the comments below. Visit our website for more information, expert advice, and recommended products to keep your skin healthy and infection-free!

Leave a Reply