Fungal infections are a common concern affecting skin health globally. These infections result from the overgrowth of fungi in warm, moist environments on the body. While often not life-threatening, untreated fungal conditions can lead to discomfort, irritation, and even secondary infections. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing these issues effectively.
This article delves into fungal infections, their impact on the skin, and the best ways to address and prevent them.
Understanding Fungal Infections and Their Impact on Skin
Fungal infections occur when microscopic fungi, including yeasts and molds, invade the skin. These organisms thrive in environments with excess moisture, such as the groin, underarms, and between the toes. Their presence can compromise the skin’s barrier function, leading to irritation, redness, and scaling.
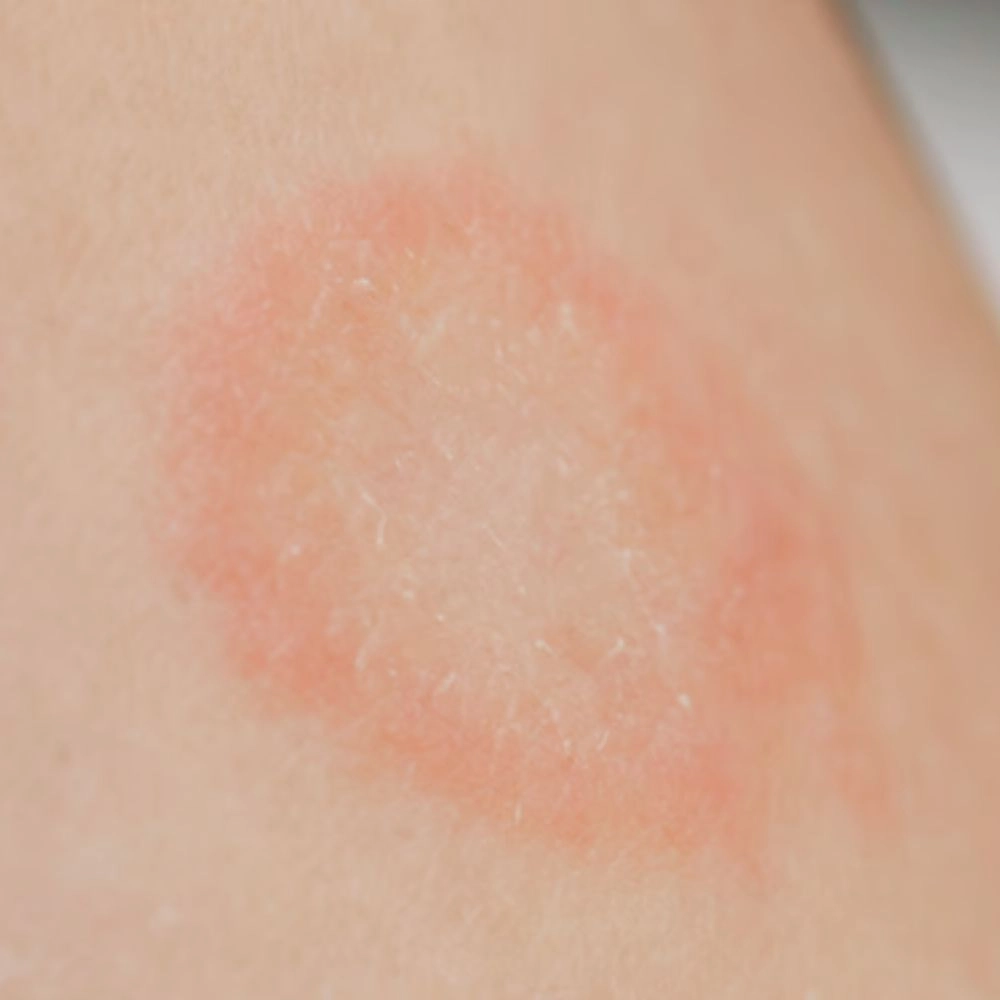
Common Types of Fungal Infections:
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): Affects the feet, causing itching, peeling, and cracked skin.
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Manifests as a circular rash with a raised border.
- Candidiasis: Results from yeast overgrowth, often in the mouth, genital area, or skin folds.
- Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis): Thickens and discolors the nails, often making them brittle.
Fungal infections can vary in severity, with some requiring simple topical treatments while others need prescription medications.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of fungal infections early is crucial for effective treatment. Symptoms depend on the type of infection but often include:

- Itching and Irritation: Persistent itching in affected areas is one of the earliest signs.
- Redness and Swelling: Inflamed patches of skin may develop, often with a defined edge.
- Scaling or Cracking: The skin may peel, flake, or crack, especially in cases like athlete’s foot.
- Discoloration: Fungal infections in nails often lead to yellowing or darkening.
If these symptoms persist or spread, consulting a dermatologist is recommended.
Treating Fungal Infections to Restore Skin Health
Effective treatment begins with proper identification. Here’s how fungal infections can be addressed:
1. Topical Antifungal Creams and Ointments
Over-the-counter products containing miconazole, clotrimazole, or terbinafine can be effective for mild cases. These creams are easy to apply and directly target the infected area.
2. Prescription Medications
For severe infections, oral antifungal drugs like fluconazole or itraconazole may be necessary. These medications work systemically to eradicate the infection from within.
3. Natural Remedies
- Tea Tree Oil: Offers antifungal properties to soothe minor infections.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Restores the skin’s pH balance to prevent fungal growth.
- Coconut Oil: Provides a moisturizing layer with mild antifungal benefits.
4. Hygienic Practices

- Regularly washing and thoroughly drying affected areas.
- Avoiding tight, non-breathable clothing that traps moisture.
Consistency in treatment is key, as fungal infections can recur if not fully eradicated.
Prevention: Protecting Your Skin Against Fungal Infections
Prevention plays a pivotal role in maintaining healthy skin. Here are some practices to adopt:
1. Keep Skin Dry and Clean
Moisture is a breeding ground for fungi. Towel off thoroughly after bathing, paying extra attention to folds and crevices.
2. Wear Breathable Fabrics
Opt for cotton or moisture-wicking materials, especially during exercise, to reduce sweat buildup.
3. Avoid Walking Barefoot in Public Areas

Fungi thrive in communal showers, locker rooms, and pools. Always wear flip-flops or water shoes in these environments.
4. Don’t Share Personal Items

Sharing towels, shoes, or grooming tools increases the risk of cross-contamination. Keep personal items separate.
5. Boost Immune Health
A strong immune system helps your body fight off fungal infections. Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many fungal infections can be treated at home, certain situations warrant professional evaluation. Contact a dermatologist if:
- The infection doesn’t improve after two weeks of treatment.
- Symptoms include severe swelling, oozing, or pain.
- Fungal growth spreads rapidly to other parts of the body.
In some cases, fungal infections can mimic other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, making an accurate diagnosis essential for effective care.
The Link Between Skin Health and Fungal Infections
Healthy skin acts as a natural barrier against harmful pathogens, including fungi. Damage to this barrier, whether through cuts, excessive sweating, or poor hygiene, can increase susceptibility. Maintaining overall skin health through hydration, a balanced diet, and regular cleansing can significantly reduce the risk of infections.
Conclusion
Fungal infections, while common, are manageable with the right knowledge and approach. By understanding the types of infections, recognizing symptoms early, and following effective treatment methods, you can maintain healthy, resilient skin. Prevention through proper hygiene and lifestyle choices plays an equally important role in minimizing recurrence.
Do you have personal tips for managing fungal infections or questions about keeping your skin healthy? Share your thoughts in the comments below or explore our website for more in-depth guides and expert advice. Let’s keep the conversation going!
Leave a Reply