Fungal infections are a widespread yet often misunderstood health issue. They affect millions worldwide, impacting the skin, nails, lungs, and even internal organs in severe cases. While many fungal infections are mild and treatable, some can become severe if left unchecked. Understanding the common types of fungal infections, their symptoms, and the treatments available is crucial for maintaining health and avoiding complications.
This guide breaks down the basics, offering insight into identifying and addressing these infections effectively.
Types of Fungal Infections
1. Superficial Infections: Skin and Nails
The most common type of fungal infections affects the skin and nails. Conditions like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and onychomycosis (nail fungus) are prevalent due to their ease of spread in warm, moist environments. These infections are usually non-life-threatening but can cause discomfort and embarrassment.
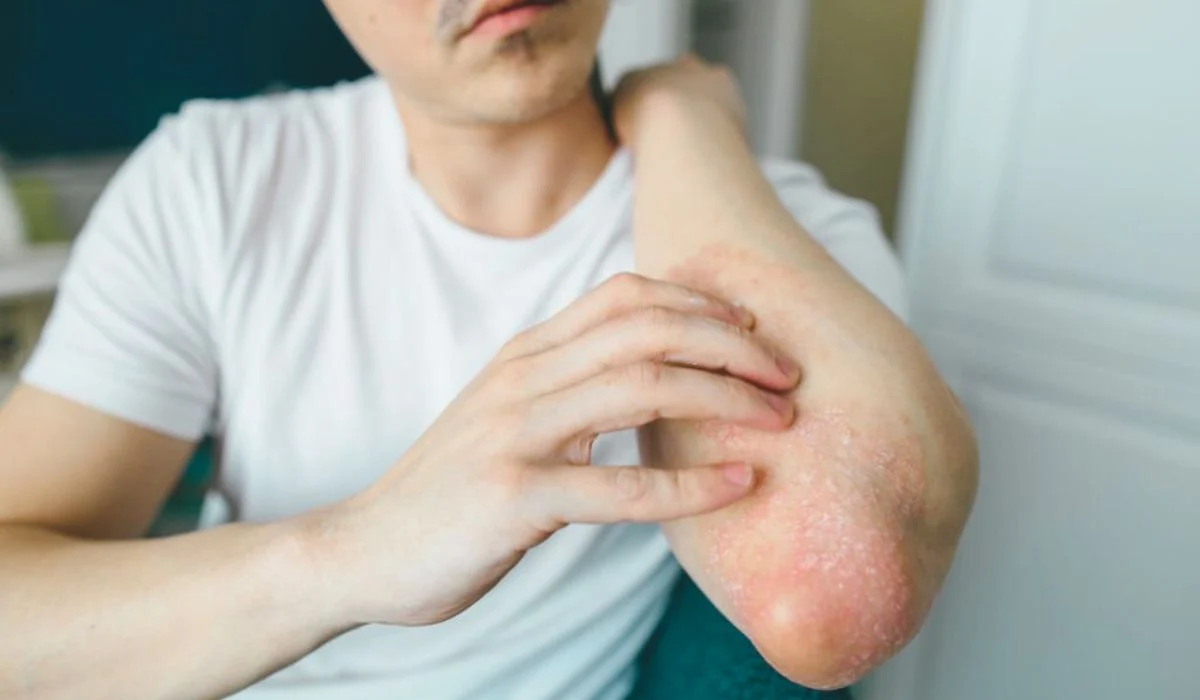
- Symptoms: Itchy, red, or scaly patches; thickened or discolored nails.
- Causes: Poor hygiene, excessive sweating, or contact with infected surfaces.
- Treatment: Topical antifungal creams, medicated nail solutions, and good hygiene practices.
2. Mucosal Infections: Mouth and Genitals
Mucosal fungal infections include oral thrush and vaginal yeast infections, often caused by the Candida species. They can result from antibiotic use, hormonal changes, or immune system imbalances.

- Symptoms: White patches in the mouth, soreness, itching, or unusual discharge in the affected areas.
- Causes: Imbalance of normal flora due to antibiotics or health conditions like diabetes.
- Treatment: Antifungal oral rinses, lozenges, and vaginal suppositories.
3. Systemic Infections: Internal Organs
Systemic fungal infections, such as aspergillosis or cryptococcosis, occur when fungi invade internal organs, posing a serious health risk. These infections are rare but more common in immunocompromised individuals.
- Symptoms: Fever, difficulty breathing, or persistent cough in lung infections.
- Causes: Inhalation of fungal spores or bloodstream infections.
- Treatment: Intravenous antifungal medications and close medical supervision.
Causes of Fungal Infections
Fungi thrive in warm, damp environments, making certain habits and conditions conducive to infections:

- Hygiene: Inadequate cleanliness or prolonged dampness can encourage fungal growth.
- Immune System Weakness: Chronic diseases like HIV, diabetes, or cancer can increase vulnerability.
- Environment: Warm, humid climates and shared spaces like gyms or swimming pools provide ideal fungal habitats.
- Medications: Antibiotics and immunosuppressive drugs can disturb the body’s natural defenses.
Diagnosing Fungal Infections
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Doctors typically perform:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/yeast-infection-diagnosis-5ad8c051312834003699dab9.png)
- Physical Examinations: Visual inspection of affected areas.
- Lab Tests: Microscopic analysis or cultures to identify the fungal species.
- Blood Tests: For systemic infections or to evaluate immune response.
Treatment Options for Fungal Infections
1. Over-the-Counter Remedies
Mild infections, such as athlete’s foot or ringworm, often respond to topical antifungal creams, powders, or sprays available without a prescription.
2. Prescription Medications
Severe or recurrent infections may require oral antifungal drugs, such as fluconazole or terbinafine, to eliminate fungi from within.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Preventing reinfection is key. Adopting habits like keeping skin dry, wearing breathable fabrics, and avoiding shared personal items can help.
4. Advanced Therapies
For systemic infections, intravenous antifungals or combination treatments are necessary, especially for immunocompromised patients.
Preventing Fungal Infections
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
- Regularly clean and dry skin folds, feet, and undergarments.
- Use antifungal powders in moist areas.
2. Boost Immunity
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Tips-to-Prevent-a-Fungal-Rash-on-Your-Face_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-99e2e91eed9649f78a1aaee3af398103.jpg)
- Eat a balanced diet, exercise, and manage stress to support immune health.
- Control underlying conditions like diabetes to reduce infection risk.
3. Avoid Contaminated Surfaces
- Wear footwear in communal showers or pool areas.
- Disinfect personal grooming tools like nail clippers or razors.
4. Know When to Seek Medical Help
If an infection persists or worsens despite treatment, consult a healthcare provider for specialized care.
Impact of Fungal Infections on Daily Life
Left untreated, fungal infections can lead to complications, including secondary bacterial infections or permanent damage to nails and skin. They can also affect self-esteem due to visible symptoms like discolored nails or rashes. Early intervention and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for maintaining both physical and emotional well-being.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Advances in medical research are improving treatment efficacy for fungal infections:
- New Antifungal Drugs: Scientists are developing medications targeting resistant fungal strains.

- Probiotics: These may help restore natural flora balance and prevent overgrowth.
- Genetic Research: Identifying genetic factors in susceptibility could lead to personalized treatments.
Conclusion
Fungal infections, while common, are manageable with the right knowledge and care. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment can prevent complications and improve recovery outcomes. Whether it’s a superficial skin issue or a more severe internal condition, understanding the basics of fungal infections is the first step toward effective management.
If you found this article helpful, let us know your thoughts! Share your experiences with fungal infections or ask any questions in the comments. Don’t forget to explore more health topics on our website for tips and insights tailored to your needs.
Leave a Reply