Fungal infections affect millions of people worldwide, ranging from mild irritations to serious health conditions. These infections occur when fungi, which are common in the environment, find a conducive host in human tissue. While some infections may only cause minor discomfort, others can escalate into significant medical concerns if not treated promptly. Identifying the symptoms and understanding the risk factors associated with fungal diseases is essential for prevention and management.
This article sheds light on the nature of fungal infections, who might be at risk, and how to recognize early warning signs for timely intervention.
What Are Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections are caused by fungi, microorganisms that thrive in diverse environments, including soil, water, plants, and the human body. Not all fungi are harmful, but certain types can infect the skin, nails, mucous membranes, and even internal organs. Common infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections, each presenting distinct symptoms.
How Fungal Infections Develop
Fungi grow best in warm, moist environments, making specific parts of the body, like feet, groin, and armpits, particularly susceptible. They can enter through minor cuts or abrasions and quickly multiply if conditions are favorable. People with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions are at higher risk of more invasive fungal diseases.
Who Is at Risk of Fungal Infections?
Although fungal infections can affect anyone, certain groups are more vulnerable due to lifestyle, health conditions, or environmental factors.
1. People with Weakened Immune Systems

Individuals undergoing chemotherapy, taking immunosuppressants, or living with chronic illnesses like HIV/AIDS are more susceptible to severe fungal infections. A weakened immune system makes it difficult for the body to fend off fungal growth.
2. Individuals with Diabetes
High blood sugar levels can create an ideal environment for fungal infections, especially in warm, moist areas. Diabetic patients often experience recurrent infections like thrush or skin rashes.
3. Athletes and Active Individuals
Frequent exposure to sweaty clothing and shared facilities such as locker rooms increases the likelihood of infections like athlete’s foot or jock itch.
4. People Living in Humid Climates

High humidity encourages fungal growth on the skin and in shoes, making fungal infections more prevalent in tropical regions.
5. Pregnant Women and the Elderly
Hormonal changes during pregnancy and reduced immune efficiency in older adults make these groups more prone to infections, such as yeast infections and toenail fungus.
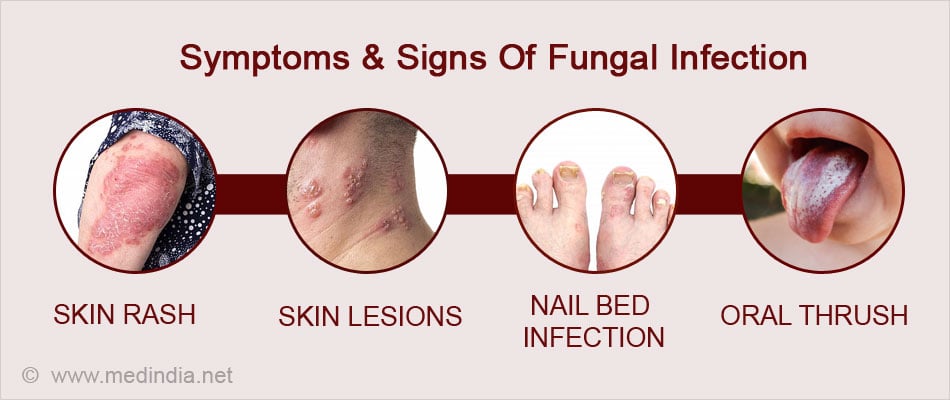
Recognizing Symptoms of Common Fungal Infections
Early identification of symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Different fungal infections manifest in unique ways, depending on the area of the body they affect.
1. Skin Fungal Infections
- Symptoms: Redness, itching, peeling, and sometimes blistering of the skin. Common infections include athlete’s foot and ringworm.
- Affected Areas: Feet, groin, underarms, or any part of the body that stays warm and moist.
2. Nail Fungal Infections
- Symptoms: Thickened, discolored, or brittle nails that may detach from the nail bed.
- Causes: Prolonged exposure to moisture and fungal spores, often from communal spaces like swimming pools.
3. Yeast Infections
- Symptoms: White patches, redness, and itching, typically in the mouth (oral thrush) or genital areas.
- Causes: Imbalance in natural flora due to antibiotic use, hormonal changes, or high sugar levels.
4. Scalp Infections
- Symptoms: Patchy hair loss, scaling, and severe itching.
- Common in: Children, often transmitted through sharing combs or hats.
5. Systemic Fungal Infections
- Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, difficulty breathing, or other severe symptoms when fungi invade the bloodstream or internal organs.
- Risk Factors: Mostly affects immunocompromised individuals and requires urgent medical attention.
Preventing Fungal Infections
Prevention is better than cure, and simple hygiene practices can go a long way in minimizing the risk of fungal infections.

1. Maintain Proper Hygiene
- Wash hands and feet regularly, especially after using public facilities.
- Dry off thoroughly after showers or swims, paying special attention to folds and crevices.
2. Wear Breathable Clothing
- Choose fabrics that allow air circulation to keep the skin dry.
- Avoid tight shoes and change socks daily to reduce moisture build-up.
3. Use Antifungal Products Proactively
- Over-the-counter sprays, powders, or creams can prevent common fungal infections in high-risk areas.
4. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
- Towels, footwear, and grooming tools can easily transfer fungal spores from one person to another.
5. Boost Immunity
- A healthy diet, adequate sleep, and regular exercise can strengthen the immune system, reducing susceptibility to infections.
Effective Treatment Options

When fungal infections occur, timely treatment can prevent complications and recurrence. Options range from home remedies to prescribed medications.
1. Topical Antifungal Creams
These are widely available for skin infections like athlete’s foot or ringworm. Examples include clotrimazole and miconazole.
2. Oral Antifungal Medications
For more severe infections, doctors may prescribe oral medications such as fluconazole or terbinafine.
3. Home Remedies
Natural remedies like diluted tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar have antifungal properties and can soothe mild symptoms.
4. Medical Consultation
Persistent or severe symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to identify the specific fungus and determine appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many fungal infections are manageable at home, some conditions require medical attention:
- Symptoms that worsen or do not improve within two weeks.
- Infections that spread rapidly or affect large areas of the body.
- Systemic infections causing fever, fatigue, or other severe symptoms.
Early diagnosis ensures effective treatment, minimizing discomfort and preventing complications.
Conclusion
Fungal infections are prevalent but preventable conditions that can affect anyone, particularly those with specific risk factors. By understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms, you can take proactive steps to avoid infections or address them early. Maintaining good hygiene, using antifungal products, and boosting immunity are simple yet effective strategies to protect yourself.
Did this guide help you better understand fungal infections? Explore our website for more health tips and resources, and share your thoughts or questions in the comments below!

Leave a Reply