The choice between hybrid cars and electric vehicles (EVs) is more relevant than ever in today’s automotive market. Both options offer greener alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered cars, but which is the right fit for your lifestyle? While hybrids combine fuel efficiency with the familiarity of internal combustion engines, EVs represent a step into the future with zero emissions and advanced technology.
This guide breaks down the differences, advantages, and potential drawbacks to help you decide which vehicle aligns best with your needs.
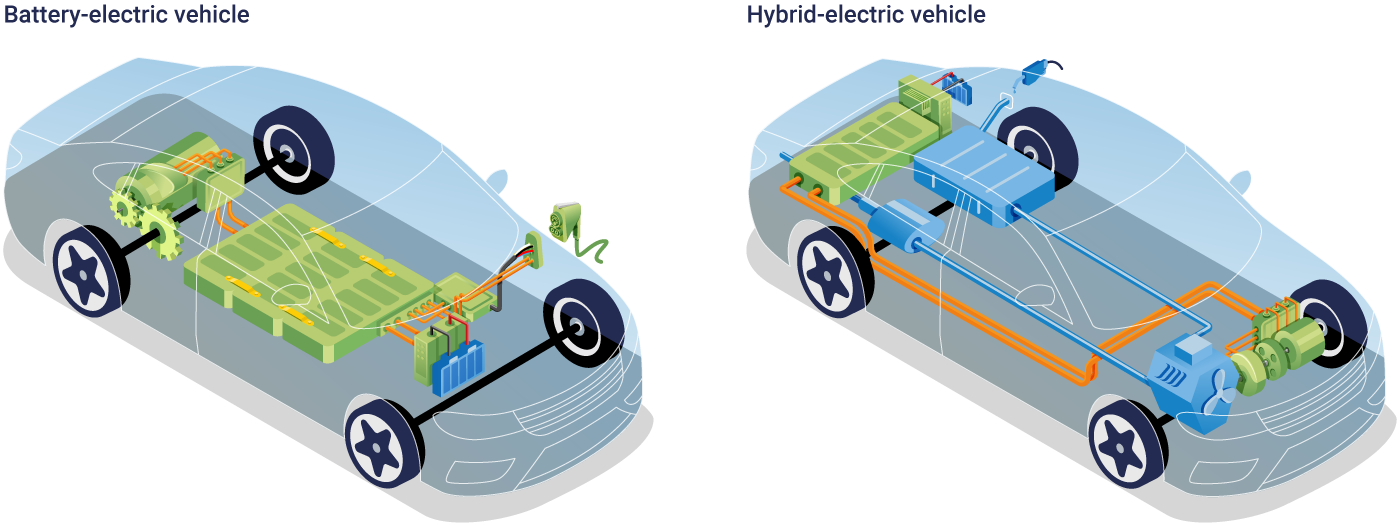
1. Understanding Hybrid Cars and Electric Vehicles
Hybrid Cars
Hybrids combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, offering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Depending on the model, hybrids may use regenerative braking to recharge their batteries, eliminating the need for external charging.
- Plug-In Hybrids: These offer larger batteries and can be charged externally, allowing for extended electric-only driving ranges.

- Standard Hybrids: These rely on their engine and braking systems to recharge, focusing on efficiency in varied driving conditions.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EVs run exclusively on electricity, powered by rechargeable batteries. These vehicles emit zero exhaust emissions, making them environmentally friendly.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Fully electric with no gasoline component.
- Extended-Range EVs: Feature small gasoline engines to generate electricity for longer trips.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial when evaluating which option best suits your lifestyle and transportation needs.
2. Advantages of Hybrid Cars
Hybrid vehicles offer several benefits for drivers who want the best of both worlds:
- Fuel Efficiency: Hybrids excel in urban environments, where frequent stops allow regenerative braking systems to recharge batteries effectively.
- Flexibility: Since they rely on gasoline and electricity, hybrids eliminate concerns about finding charging stations during long trips.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Hybrids are generally less expensive than EVs, making them accessible for budget-conscious buyers.
- Transition-Friendly: For those hesitant to switch entirely to electric driving, hybrids provide a comfortable middle ground.

Drivers with diverse commuting patterns or limited access to charging infrastructure may find hybrids more practical.
3. Advantages of Electric Vehicles

Electric cars bring unique advantages, particularly for those focused on sustainability and cutting-edge technology:
- Zero Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe pollution, contributing to cleaner air and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electricity is typically cheaper than gasoline, and EVs have fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance expenses.
- Innovative Features: Many EVs come with advanced technology, including over-the-air updates, autonomous driving capabilities, and app-controlled features.
- Incentives and Tax Benefits: Governments often offer rebates, tax credits, and other perks to encourage EV adoption.
For eco-conscious consumers or those with access to reliable charging infrastructure, EVs are an appealing choice.
4. Key Considerations When Choosing
When deciding between a hybrid and an electric vehicle, consider the following factors:
- Driving Habits:
- Frequent long-distance drivers may benefit from a hybrid’s extended range and refueling convenience.
- City commuters with short trips may find an EV’s zero-emission capabilities and lower running costs more suitable.
- Infrastructure:
- Access to charging stations is critical for EV owners. Without a home charging setup, owning an electric car may be challenging.
- Hybrids, which don’t rely on external charging, are a better fit for areas with limited infrastructure.
- Initial Cost:
- While EVs may have higher upfront costs, long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can offset this expense.
- Hybrids often have a lower purchase price, making them more affordable for those new to green technology.
- Environmental Goals:
- For individuals aiming to minimize environmental impact, EVs offer unparalleled benefits.
- Hybrids still contribute to lower emissions compared to traditional cars, making them a solid alternative.
5. The Future of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles

Both hybrids and EVs play pivotal roles in the transition to sustainable transportation. However, the future trajectory of these technologies differs:
- Hybrids as Transitional Vehicles:
- As EV infrastructure continues to expand, hybrids provide a bridge for drivers hesitant to fully embrace electric mobility.
- Innovations in plug-in hybrids extend electric ranges, making them increasingly competitive.
- EV Dominance on the Horizon:
- With advancements in battery technology and a global push for renewable energy, EVs are poised to dominate the automotive landscape.
- Governments worldwide are setting ambitious targets for phasing out internal combustion engines, further accelerating EV adoption.
The interplay between these technologies ensures consumers have diverse options tailored to their evolving preferences and needs.
Conclusion
Choosing between a hybrid and an electric vehicle boils down to lifestyle, priorities, and available resources. Hybrids offer convenience, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for drivers seeking gradual adoption of green technology. On the other hand, EVs deliver cutting-edge innovation, environmental benefits, and long-term savings, perfect for those ready to embrace the future.
Which option aligns with your driving needs? Let us know your thoughts in the comments and explore more about hybrid and electric vehicles on our website. Your journey toward a sustainable driving future starts here!

Leave a Reply