When it comes to repairing household appliances, electronic devices, or even automobiles, one of the first concerns is often the cost. Understanding what influences repair costs can help you make informed decisions and budget effectively. Repair fees can vary widely, depending on the type of item, the extent of damage, and the expertise required to fix it. By gaining insight into the factors that determine service charges, you’ll be better equipped to select the right provider and ensure you’re paying a fair price. In this guide, we’ll break down the key elements that influence repair costs and share tips on how to save money without compromising quality.
Type of Item Being Repaired
The nature of the item requiring repair significantly impacts the service fee. Complex devices or specialized items often come with higher costs due to their intricate mechanisms. For example:
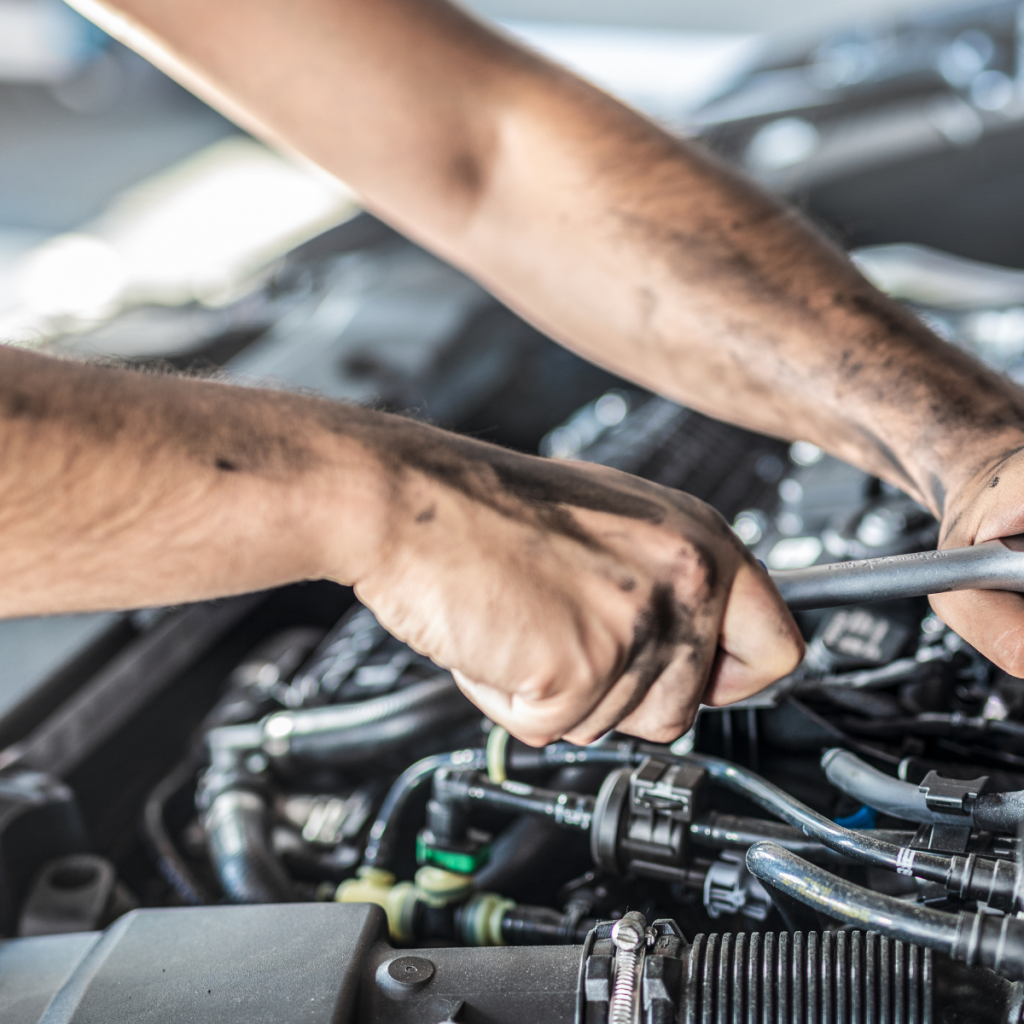

Electronics: Repairs for laptops, smartphones, or televisions involve delicate components, which may demand advanced tools and skills.
Home Appliances: Fixing large items like refrigerators, washing machines, or HVAC systems can be expensive due to labor intensity and part costs.
Vehicles: Automotive repairs, such as fixing engines or brakes, often require specialized diagnostics and can incur significant charges.
Extent of Damage
The severity of the problem plays a critical role in determining the repair fee. Minor issues, such as replacing a battery or fixing a loose wire, typically cost less. However, major damages that require extensive labor, part replacements, or advanced diagnostics will increase the overall expense.
For example:
Replacing a cracked smartphone screen may be less costly than repairing water damage, which could involve multiple components.
A refrigerator requiring a new motor will be more expensive to fix than one needing only a thermostat adjustment.
Parts and Material Costs
Replacement parts can significantly influence the total repair bill. The price of materials depends on factors such as:
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Parts: Using OEM parts often costs more but ensures compatibility and quality.
Aftermarket Parts: These are usually more affordable but might not meet the same standards as OEM parts.
Scarcity of Components: Hard-to-find or discontinued parts can drive up repair costs.
For example, vintage electronics or older car models may require custom-made components, increasing fees.
Labor Charges
Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the repair and the expertise required. Skilled technicians with certifications may charge higher fees, but their work is often more reliable. Factors influencing labor charges include:
Hourly Rates: Some repair services charge by the hour, which can quickly add up for complicated tasks.
Flat Fees: For straightforward repairs, flat-rate pricing offers predictability and transparency.
Regional Variations: Labor costs tend to be higher in urban areas compared to smaller towns.
Diagnostic Fees
Many service providers charge an upfront diagnostic fee to identify the problem before offering a solution. This fee compensates for the time and expertise required to assess the issue. Some shops waive the diagnostic fee if you proceed with the repair, while others may include it in the final bill.
Warranty and Service Guarantees
Choosing a repair service that offers warranties or guarantees can affect costs. While services with warranties may be slightly more expensive upfront, they provide peace of mind and protection against future issues. Key considerations include:
Duration of Warranty: Longer warranties may indicate higher initial costs but greater value over time.
Scope of Coverage: Comprehensive warranties that include labor and parts often justify a higher service fee.
Location of the Repair Service
The geographic location of the repair shop or service provider can significantly impact costs. Factors include:
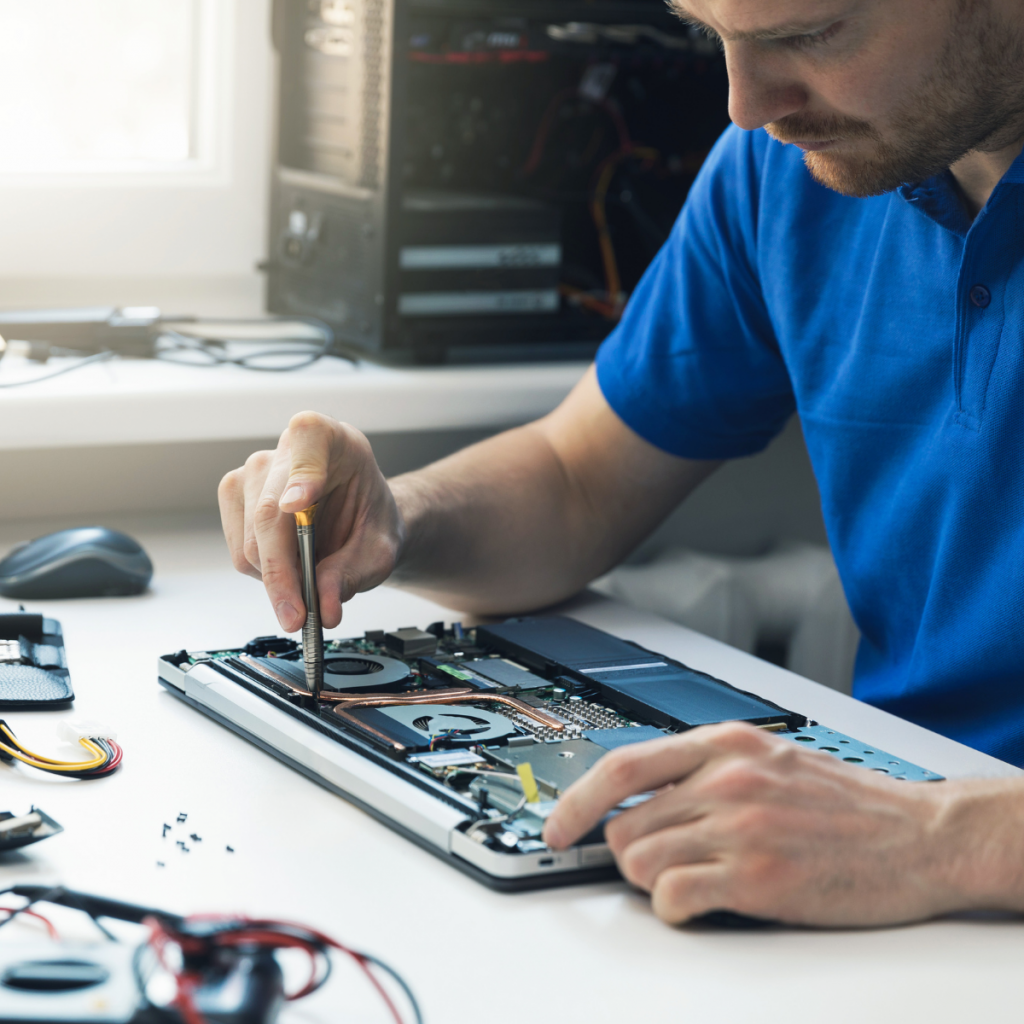

Urban vs. Rural Areas: Repair costs in metropolitan regions are typically higher due to increased overheads and demand.
On-Site Services: Mobile repair technicians who visit your home or office may charge a convenience fee.
Distance from Service Center: Additional travel expenses might be included for repairs conducted far from the provider’s base.
Urgency of the Repair
Rush repairs or same-day services often come with premium pricing. If you need your device or appliance fixed immediately, expect to pay more for expedited attention. Planning repairs in advance or opting for standard service times can help reduce costs.
Seasonal Demand
Repair costs can fluctuate based on seasonal demand. For example:
HVAC repairs are often more expensive during peak summer or winter months when demand for heating or cooling services is high.
Electronics repairs may spike during holiday seasons when technicians are busier handling increased workloads.
Technician Expertise and Certification
Highly skilled or certified technicians often charge more for their services, but they bring added assurance of quality. For instance:
Specialized Training: A technician trained to repair specific brands or models may demand higher fees.
Reputation and Experience: Established repair centers with strong customer trust often justify their premium pricing.
Hidden Fees and Additional Costs
Some repair services include hidden charges that can inflate the final bill. These might include:
Disposal fees for old or damaged parts.
Extra charges for testing or calibration after repairs.
Administrative fees for processing paperwork or warranties.
Always request a detailed estimate upfront to avoid surprises.
Technological Advancements and Tools Used
Modern tools and technology used in repair services can impact pricing. For instance, services that employ advanced diagnostic machines or laser repair tools may charge higher fees. While these methods may cost more, they often ensure precision and reduce the risk of recurring issues.
Service Provider Policies
Different repair shops have varying pricing structures and policies, such as:
Flat-Rate Pricing: Transparent fees for specific repairs.
Variable Pricing: Fees adjusted based on the complexity or duration of the repair.
Comparing multiple service providers can help you find one that fits your budget.
Age and Model of the Device
Older models or discontinued items often cost more to repair due to the difficulty in sourcing compatible parts. Similarly, newer, high-tech devices may require specialized skills and tools, increasing the service fee.
DIY Repairs vs. Professional Services
Attempting DIY repairs can save money upfront but may lead to higher costs if mistakes cause further damage. Professional services ensure proper handling, reducing the likelihood of additional expenses.
Tips for Managing Repair Costs
- Get Multiple Estimates: Comparing quotes from different providers can help you secure the best deal.
- Opt for Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance reduces the likelihood of costly repairs.
- Check Warranties: Determine if your device is still under manufacturer warranty to save on repair fees.
- Research Service Providers: Look for reputable repair shops with clear pricing and excellent reviews.
- Negotiate Costs: Some providers may be willing to lower fees, especially for recurring customers.
Conclusion
Repair costs are influenced by a variety of factors, including the type of item, extent of damage, and expertise required. By understanding these variables, you can make informed decisions about when and where to seek repairs. Whether it’s a minor fix or a complex issue, being aware of the factors that impact service fees will help you budget wisely and avoid overpaying. Remember, investing in quality repairs ensures better performance and extends the life of your valuable devices and appliances.

Leave a Reply