Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs due to an excess buildup of uric acid in the body, leading to the formation of sharp crystals in joints. This condition is known for its sudden, intense pain and discomfort. Detecting gout symptoms early is crucial to managing the disease effectively and preventing long-term complications. In this article, we will explore the telltale signs of gout, its progression, and practical ways to identify the condition before it becomes severe. Understanding these symptoms can empower individuals to seek timely treatment and adopt preventive strategies.
What Is Gout?
Gout primarily affects joints, causing inflammation and severe pain. It most commonly targets the big toe but can also involve other joints like ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers. This condition often develops in episodes or flare-ups, making early recognition of symptoms vital for management.
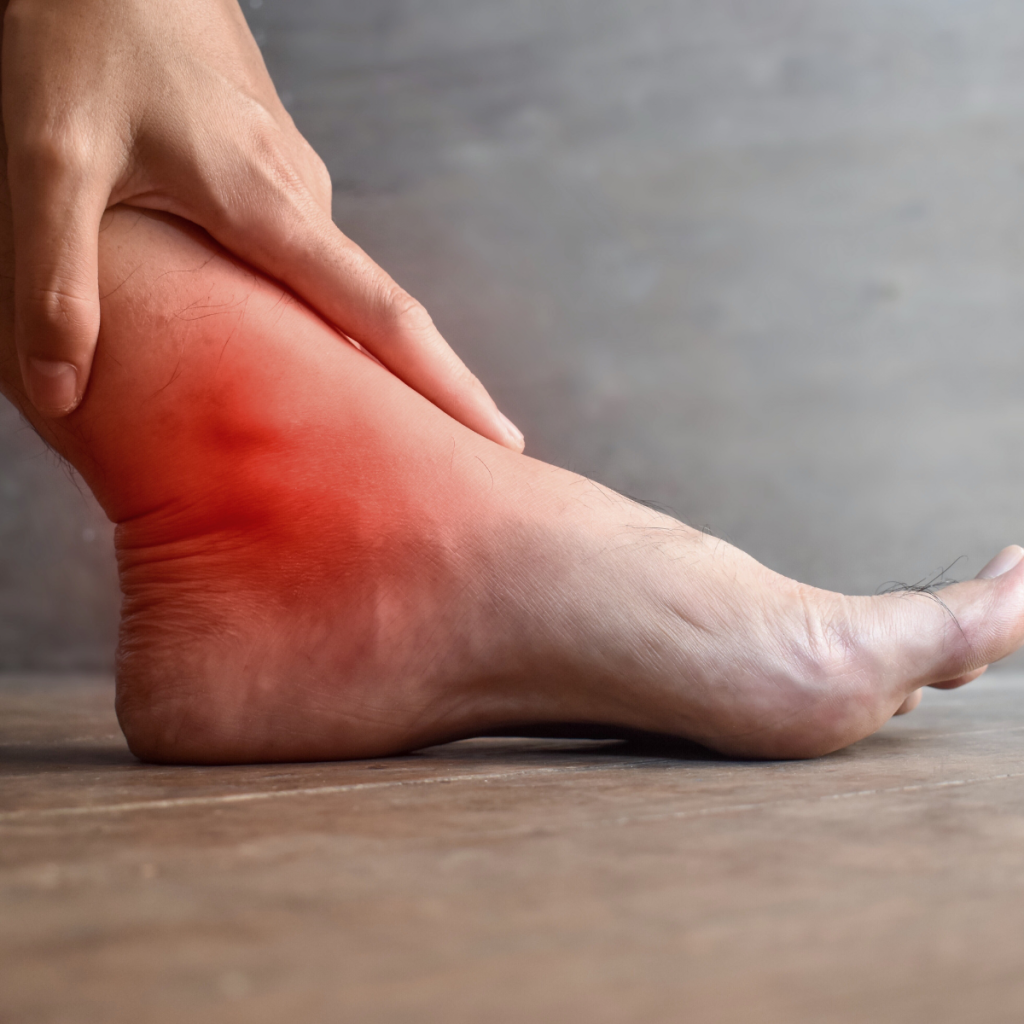
Early Symptoms of Gout
Detecting gout in its initial stages can prevent irreversible damage to joints and tissues. Below are some early warning signs:
1. Intense Joint Pain
Gout attacks often start suddenly, usually during the night. The pain is typically severe and concentrated in one joint, with the big toe being the most common site. People often describe the sensation as throbbing, crushing, or burning.
2. Swelling Around the Joint
Inflammation causes noticeable swelling in the affected area. This swelling can appear rapidly, making the joint look larger than usual and sometimes even disfigured during a flare-up.
3. Warmth and Redness
The inflamed joint often feels warm to the touch and may appear reddish or purplish. These signs are caused by the immune system’s response to the uric acid crystals.
4. Limited Joint Movement
As gout progresses, joint stiffness may develop, making it challenging to move or flex the affected joint comfortably. This stiffness can persist even after the pain subsides.
Recurring Symptoms of Gout
If untreated, gout can progress to recurrent episodes. These recurring symptoms include:
1. Prolonged Discomfort
After the acute pain subsides, some individuals experience lingering discomfort in the affected joint. This discomfort can last for several days or weeks.
2. Development of Tophi
Chronic gout may lead to the formation of tophi, which are lumps of uric acid crystals that develop under the skin. These are usually found on fingers, elbows, and the outer ear.
3. Persistent Swelling
Over time, swelling becomes more frequent and less dependent on flare-ups. This can indicate chronic inflammation and ongoing joint damage.
4. Joint Deformity
Untreated gout can lead to permanent damage and deformities in the affected joints, limiting mobility and functionality.
Common Triggers for Gout Symptoms
Certain factors can worsen gout symptoms or trigger flare-ups. These include:
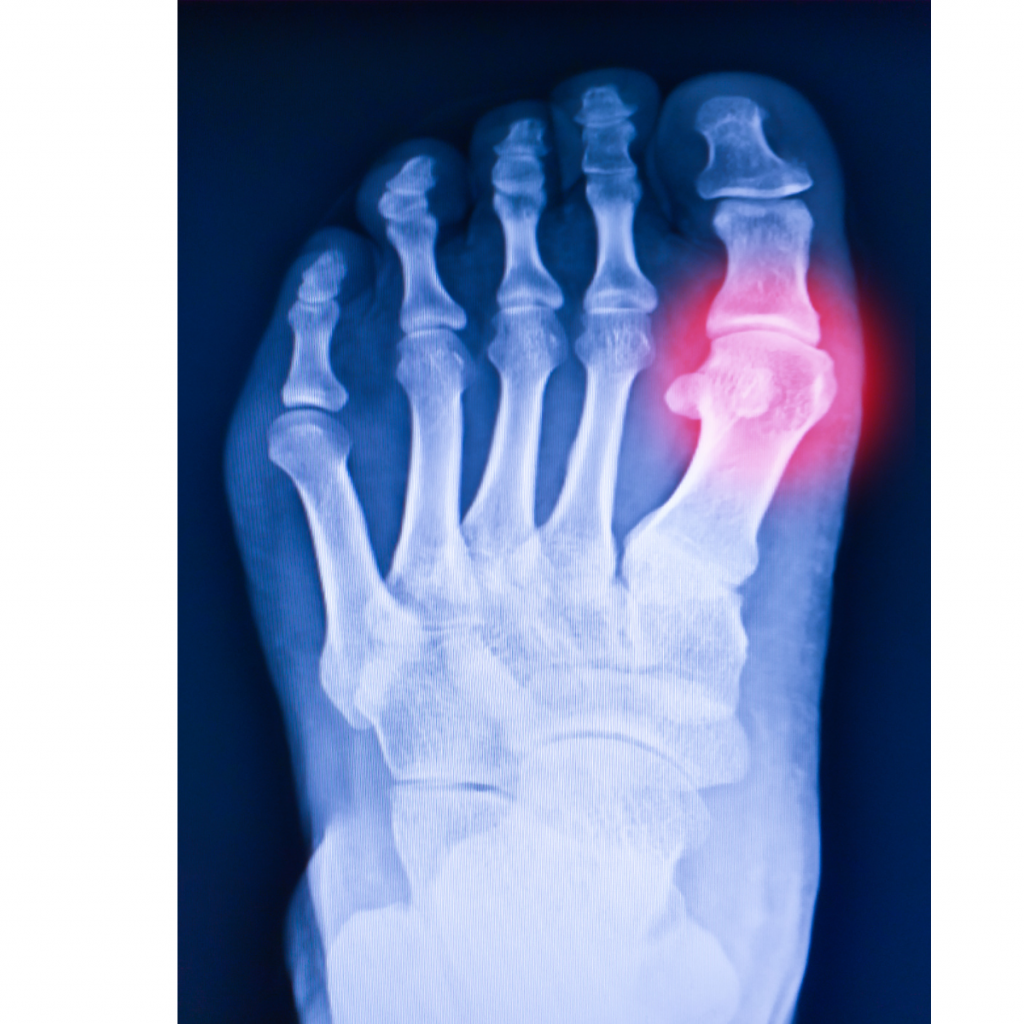
- Dietary Habits: Consuming purine-rich foods like red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks increases uric acid levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol, especially beer, impairs the body’s ability to eliminate uric acid.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can contribute to a higher likelihood of gout attacks.
- Dehydration: Lack of hydration concentrates uric acid in the bloodstream, heightening the risk of crystal formation.
Differentiating Gout from Other Conditions
Gout symptoms can mimic those of other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Understanding key differences can aid in accurate detection:
- Sudden Onset: Gout pain develops abruptly, unlike rheumatoid arthritis, which progresses gradually.
- Asymmetrical Pain: Gout typically affects one joint at a time, while other forms of arthritis often involve multiple joints.
- Visible Tophi: The presence of tophi is unique to gout and doesn’t occur in other types of arthritis.
How Is Gout Diagnosed?
If you suspect gout, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for confirmation. Doctors use various methods to diagnose gout:
- Physical Examination: Swelling, redness, and tenderness are observed in the affected joints.
- Blood Tests: Elevated uric acid levels can indicate gout, but not everyone with high uric acid develops symptoms.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: A sample of fluid is drawn from the joint to detect uric acid crystals under a microscope.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds or X-rays may be used to assess joint damage or the presence of crystals.
Why Early Detection Matters
Recognizing gout symptoms early allows individuals to take proactive steps to manage the condition. Early intervention can:
- Reduce the severity of flare-ups.
- Prevent permanent joint damage.
- Minimize the risk of kidney stones caused by excess uric acid.
- Improve overall quality of life by controlling symptoms effectively.
Effective Ways to Manage Gout Symptoms
Once diagnosed, managing gout involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and preventive strategies:
1. Follow a Gout-Friendly Diet
Avoid high-purine foods and incorporate low-purine options such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit alcohol and sugary drinks to maintain balanced uric acid levels.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking sufficient water helps flush out uric acid and reduces the risk of crystal formation.
3. Take Medications as Prescribed
Doctors may recommend anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or urate-lowering therapies to control symptoms and reduce uric acid levels.
4. Exercise Regularly
Low-impact exercises like swimming or walking can improve joint mobility and reduce inflammation.
5. Monitor Triggers
Keep track of dietary habits and lifestyle choices that may trigger flare-ups. Identifying these patterns can help prevent future attacks.
Home Remedies for Gout Relief
While professional medical care is crucial, these remedies can provide temporary relief during a flare-up:
- Cold Compress: Applying an ice pack reduces pain and inflammation.
- Rest: Avoid placing weight on the affected joint to minimize discomfort.
- Cherries: Eating cherries or drinking cherry juice may lower uric acid levels naturally.
Long-Term Management Tips
Gout is a chronic condition, but with consistent effort, its impact can be minimized. Consider the following for long-term management:
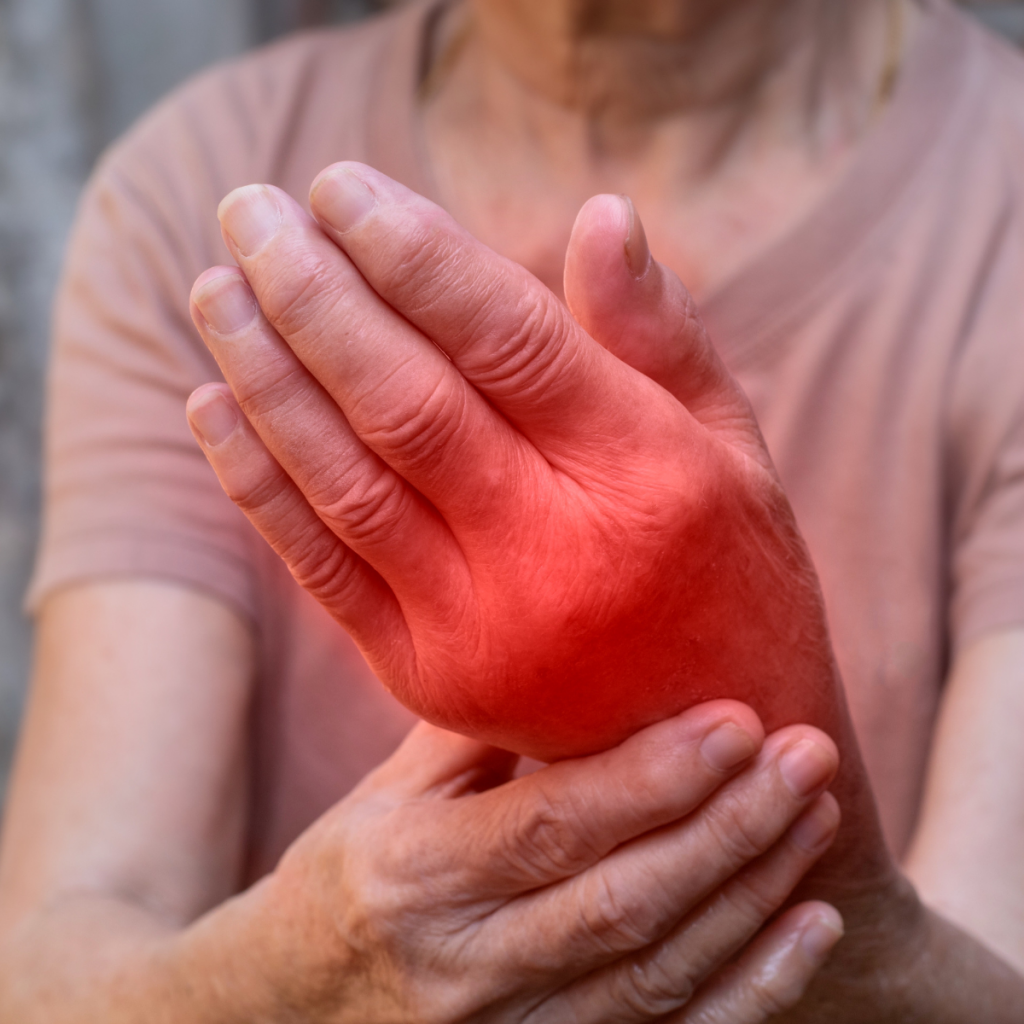
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Get regular checkups to monitor uric acid levels.
- Educate yourself about the condition to make informed decisions about care.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical care if:
- Pain and swelling become unbearable.
- Flare-ups occur more frequently.
- Symptoms spread to multiple joints.
Conclusion
Detecting gout symptoms early is the key to avoiding severe complications and preserving joint health. By recognizing warning signs, identifying triggers, and seeking timely treatment, you can effectively manage this condition and maintain an active lifestyle.
Have you or someone you know experienced gout symptoms? Share your thoughts and tips in the comments! Explore more informative articles on our website and learn how to take control of your health today.

Leave a Reply