Gout is a form of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain, redness, and swelling in the joints, particularly the big toe. This condition occurs when uric acid builds up in the blood and forms crystals in the joints. While gout can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, living with this condition requires careful attention to diet, medication, and overall health. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or have been managing gout for years, understanding how to live well with this condition is key to reducing flare-ups and improving quality of life.
In this article, we’ll explore essential tips for living with gout and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. From dietary choices to exercise and stress management, we will guide you through the steps necessary to manage gout and live pain-free. Incorporating these lifestyle changes can help you keep gout symptoms at bay and lead a more comfortable life.
Understanding Gout and Its Causes
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks. Under normal circumstances, uric acid is eliminated from the body through urine. However, if the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys can’t process it efficiently, the acid builds up in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints.
These crystals can cause intense pain and swelling, triggering a gout attack. While anyone can develop gout, it is more common in men and those with a family history of the condition. Factors such as obesity, high alcohol consumption, certain medications, and a diet rich in purines can increase the risk of gout attacks.
The Importance of a Gout-Friendly Diet
One of the most crucial aspects of managing gout is making dietary changes. Foods high in purines, which increase uric acid production, should be avoided or minimized. These include red meat, organ meats (liver, kidneys), shellfish, and certain types of fish (such as sardines and anchovies). Alcohol, particularly beer, can also elevate uric acid levels, so limiting intake is important for gout management.
Instead, focus on consuming low-purine foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. These foods help keep uric acid levels in check. Cherries, in particular, have been shown to reduce the frequency of gout attacks due to their anti-inflammatory properties, so incorporating them into your diet can be highly beneficial.
Staying well-hydrated is also essential. Drinking plenty of water helps the kidneys flush out excess uric acid, preventing it from accumulating in the joints. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day. Additionally, avoiding sugary drinks and caffeine can also help maintain a healthy uric acid level.
Exercise and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is another key component of managing gout. Obesity increases the risk of developing gout and can make symptoms worse by putting additional stress on the joints. If you’re overweight, losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks.
Regular physical activity is also beneficial for those with gout. Exercise helps improve joint flexibility, strengthens muscles, and supports weight loss. However, it’s important to avoid high-impact activities or exercises that put excessive strain on the joints, especially during an active gout flare-up. Opt for low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling to stay active without exacerbating symptoms.
Medication and Medical Management
For individuals with frequent or severe gout attacks, medication is often necessary. Your doctor may prescribe medications to reduce inflammation and pain during flare-ups, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or colchicine. These medications can help relieve symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
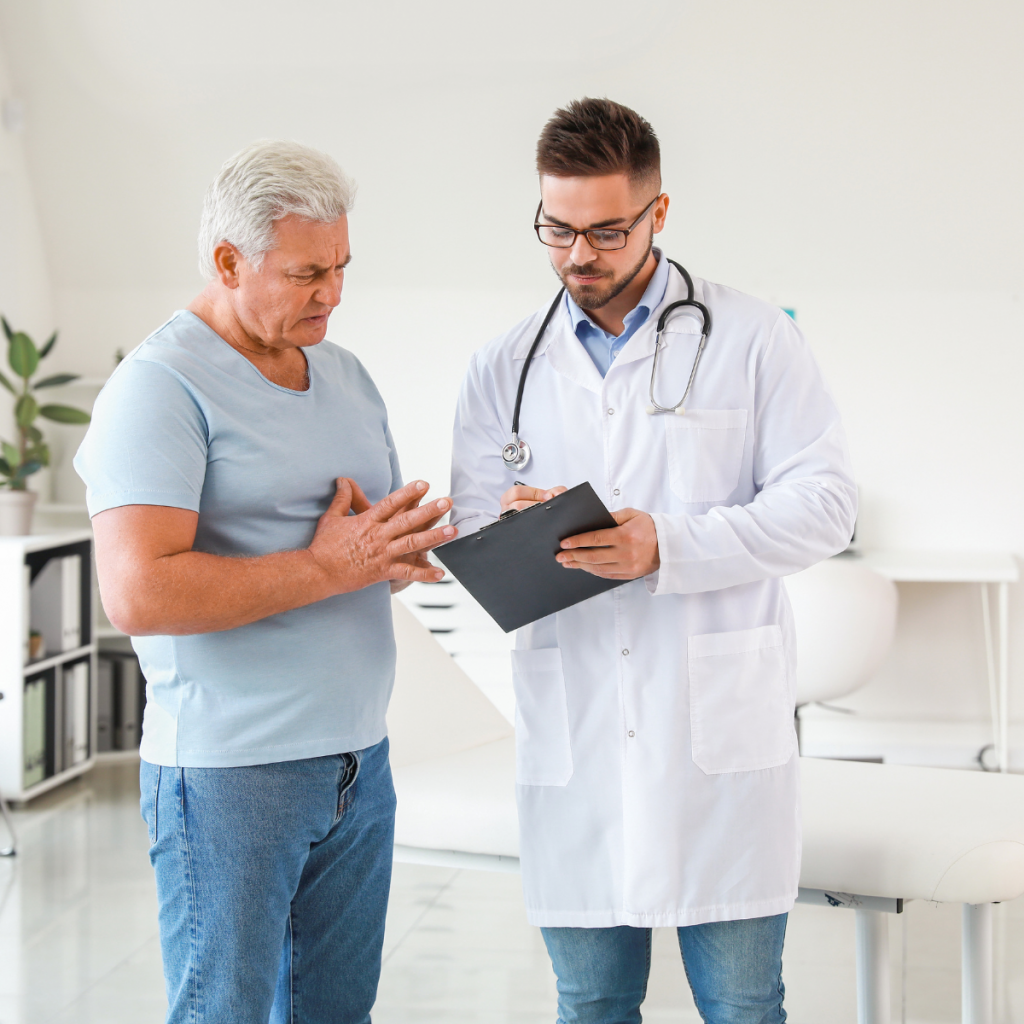

In addition to pain relief medications, long-term management may involve drugs that reduce uric acid levels in the blood. These medications, such as allopurinol or febuxostat, work by blocking the production of uric acid, preventing future gout attacks. It’s important to take these medications as prescribed, even if you are not experiencing symptoms, to reduce the risk of recurring gout flare-ups.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor uric acid levels and adjust medications if necessary. Your doctor can also help you manage other health conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or kidney problems, which can exacerbate gout.
Stress Management
Living with gout can be stressful, especially during painful flare-ups. Stress can also trigger gout attacks by affecting the body’s ability to manage uric acid levels. Therefore, managing stress is a critical part of maintaining a healthy lifestyle with gout.
Engaging in stress-relieving activities like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or even simple relaxation techniques can help reduce the risk of gout attacks. Regular relaxation and mindfulness practices have been shown to lower stress hormones and help the body better cope with pain and discomfort.
Sleep and Rest
Adequate rest is essential for managing gout and maintaining overall health. Chronic sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system, increase stress levels, and contribute to inflammation, all of which can make gout flare-ups more frequent. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your body’s ability to repair and heal.

During a gout attack, it’s important to rest the affected joint as much as possible to avoid further irritation. Elevating the joint and applying ice can also help reduce swelling and provide relief.
Avoiding Triggers and Monitoring Symptoms
Understanding and avoiding gout triggers is vital for preventing flare-ups. Certain foods, beverages, and lifestyle habits can increase uric acid levels in the blood, so it’s essential to be mindful of these triggers. In addition to dietary restrictions, managing alcohol consumption and staying hydrated are key strategies for reducing uric acid levels.
Monitoring your symptoms regularly and keeping track of when flare-ups occur can also help you identify patterns and triggers specific to your condition. Keeping a diary of your diet, physical activity, and symptoms can provide valuable insights into what may be causing gout attacks and help you make adjustments to prevent future flare-ups.
Living a Full Life with Gout
While living with gout may require some adjustments, it is entirely possible to maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle. By focusing on a healthy diet, regular exercise, proper medication, stress management, and lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce the impact of gout on your life.
Remember, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to create a personalized plan for managing gout. With the right strategies in place, you can minimize flare-ups, protect your joints, and continue to enjoy the activities and hobbies you love.
Conclusion: Embrace a Gout-Friendly Lifestyle
Managing gout requires a multifaceted approach that combines proper diet, medication, physical activity, and stress management. By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can control your symptoms and prevent long-term complications. Living with gout doesn’t mean you have to limit your quality of life – with the right care and lifestyle adjustments, you can live comfortably and healthily.
If you found these tips helpful or have any additional questions about managing gout, feel free to reach out. Visit our website for more helpful resources and support on how to live your best life while managing gout effectively!
Leave a Reply