Gout is a painful and potentially debilitating form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals build up in the joints, causing inflammation and intense pain. While many people may only experience occasional flare-ups, gout can lead to serious long-term complications if left untreated. The symptoms of gout, such as swelling, redness, and sharp pain, are warning signs that should not be ignored. Over time, untreated gout can cause irreversible damage to joints, kidneys, and other organs. In this article, we will explore the dangerous complications associated with gout, why it’s important to seek early treatment, and how you can manage the condition effectively to prevent further health risks.
Ignoring gout symptoms not only worsens the pain but can also result in a range of severe health complications that may impact your overall well-being. From kidney stones to joint deformities, the consequences of neglecting proper gout treatment can be devastating. By recognizing the signs early and addressing the root causes of gout, you can prevent these complications and maintain a healthier, pain-free life.
What Is Gout and Why Does It Occur?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that develops when there is an excessive buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream. Uric acid is a natural waste product that the body produces when it breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks. Normally, uric acid is filtered out by the kidneys and excreted through urine. However, when the kidneys cannot process uric acid properly, or when the body produces too much of it, crystals of uric acid can form and accumulate in the joints, causing painful flare-ups.
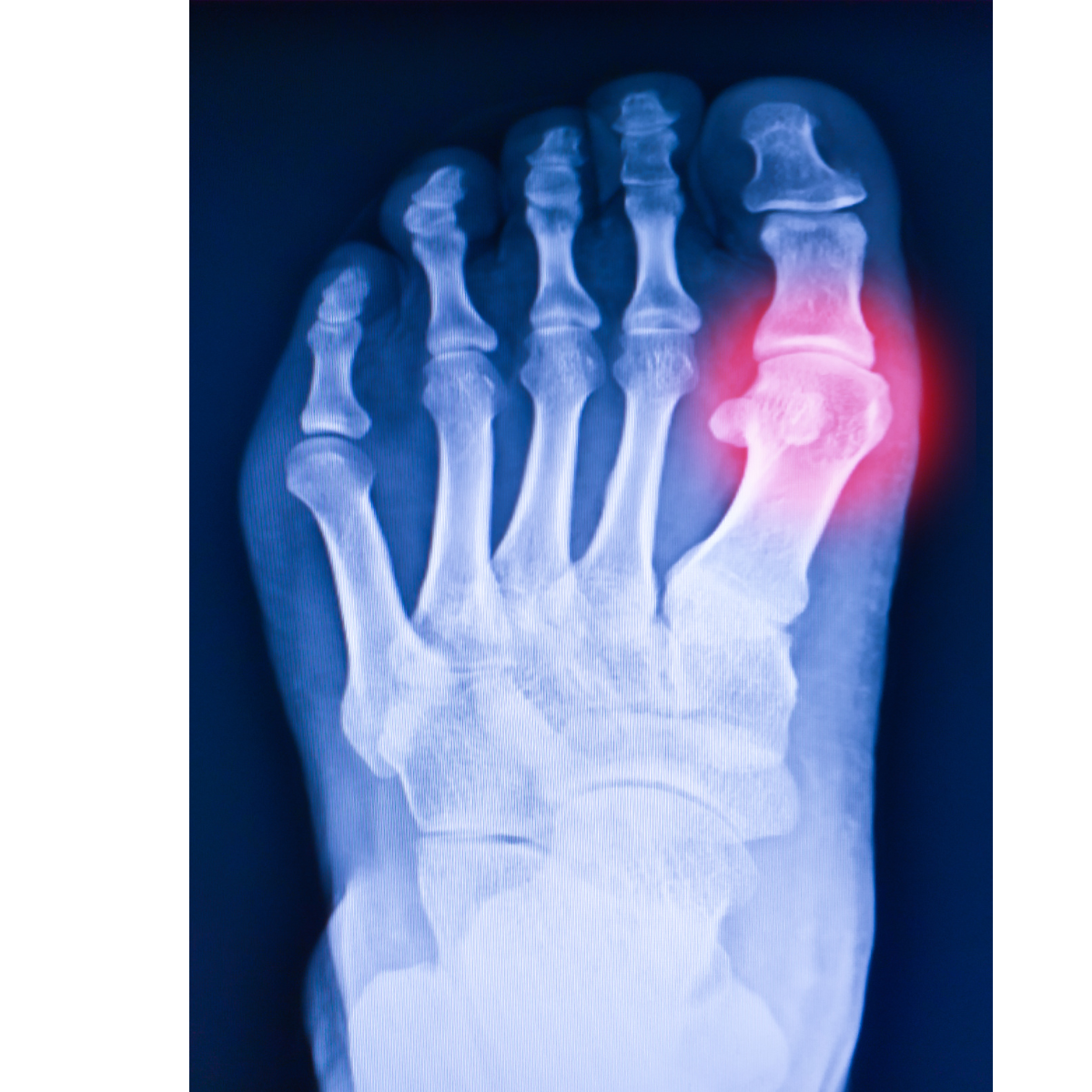
These crystals most commonly affect the big toe, but gout can also impact other joints such as the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists. The inflammation caused by the crystals triggers intense pain, redness, and swelling, and the affected area can feel extremely sensitive to touch. Without proper treatment, the risk of gout complications increases significantly.
Complications of Untreated Gout
- Joint Damage and Deformities
One of the most common long-term complications of untreated gout is joint damage. As uric acid crystals continue to accumulate, they can cause chronic inflammation in the affected joints. Over time, this inflammation damages the joint tissues, leading to deformities and reduced mobility. This is often referred to as “tophi,” which are lumps that form beneath the skin due to the accumulation of urate crystals.
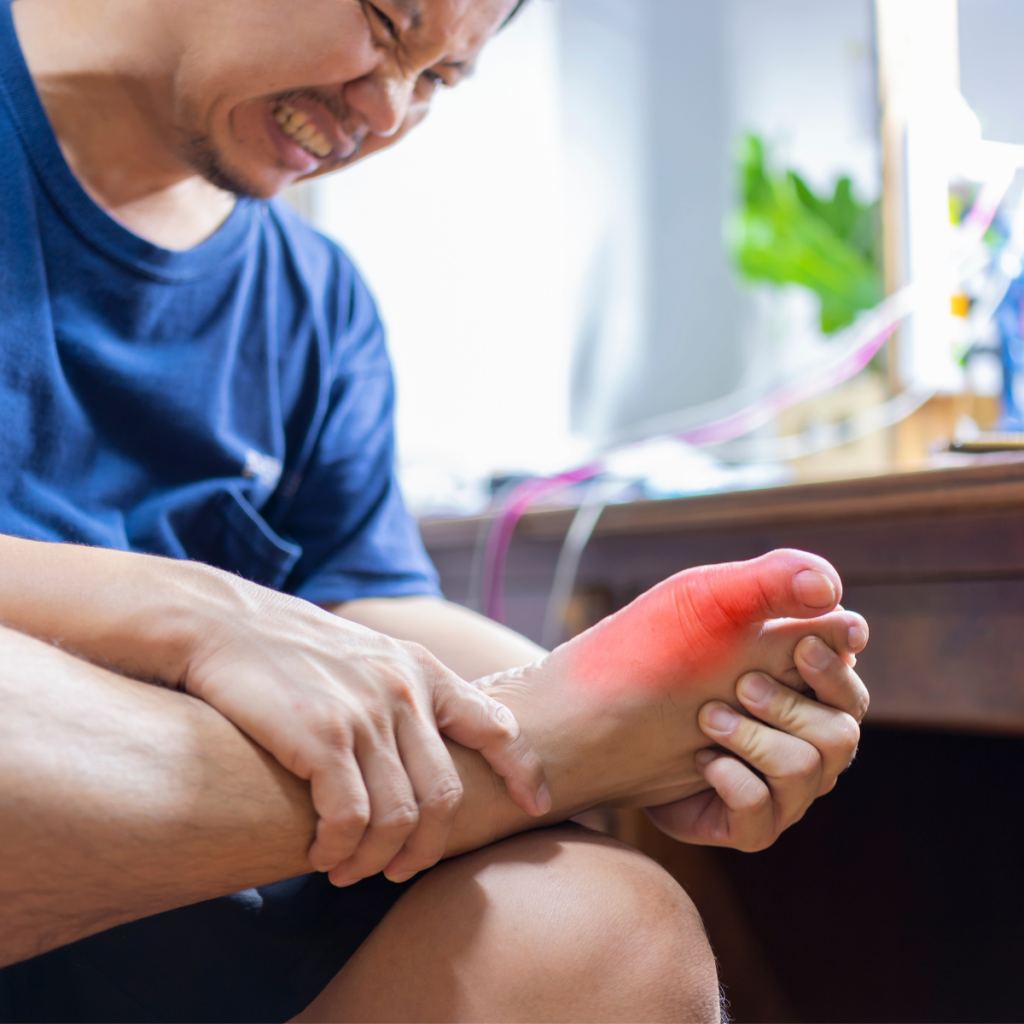

The affected joints become stiff, swollen, and painful, and the individual may lose the ability to perform everyday activities without discomfort. If left untreated, gout can severely impair the function of the affected joints, making it difficult to walk, grip objects, or perform basic movements.
- Kidney Stones
Gout is not only harmful to the joints but also to the kidneys. The excess uric acid in the bloodstream can form crystals that accumulate in the kidneys, leading to the formation of kidney stones. Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that can cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and urinary issues. The process of passing a kidney stone can be excruciating, and large stones may require surgical removal.
In addition to being painful, kidney stones caused by gout can cause long-term kidney damage, leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure if not addressed. Individuals with gout are at a higher risk of developing kidney stones, making it crucial to manage uric acid levels to protect kidney function.
- Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is another serious complication that can arise from uncontrolled gout. The constant buildup of uric acid can gradually damage the kidneys over time, impairing their ability to filter waste and toxins from the blood. As kidney function declines, waste products and excess fluids accumulate in the body, leading to dangerous complications such as high blood pressure, fluid retention, and electrolyte imbalances.
If CKD progresses to the advanced stages, it may result in kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Early detection and management of gout are key to preventing kidney disease and preserving kidney function.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Recent research has revealed that gout may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. The inflammation caused by uric acid crystals may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition in which the arteries become clogged with fatty deposits. This can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
Furthermore, individuals with gout often have other risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes. This combination of factors can elevate the likelihood of developing heart-related complications, making it essential to address gout and manage its symptoms to reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Recurrent Gout Flare-Ups
Without proper management, gout flare-ups can become more frequent and severe over time. What may start as occasional attacks can escalate into chronic, recurring episodes of pain and inflammation. These recurrent flare-ups can become more difficult to treat and may require stronger medications or more aggressive interventions.
The longer gout is left untreated, the more likely it is that flare-ups will occur more often, causing persistent pain and discomfort. This can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, leading to physical limitations, emotional distress, and even depression.
How to Prevent Gout Complications
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment
The key to preventing the dangerous complications of gout is early diagnosis and treatment. If you experience symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, or redness, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider as soon as possible. Gout can be diagnosed through blood tests, urine tests, and joint fluid analysis, and prompt treatment can help reduce inflammation and lower uric acid levels.
- Medication Management
There are several medications available that can help manage gout and prevent complications. These include anti-inflammatory drugs such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine, which help reduce pain and swelling during flare-ups. Additionally, medications like allopurinol or febuxostat can lower uric acid levels in the blood, preventing future gout attacks and reducing the risk of kidney stones and joint damage.
- Dietary Modifications
Diet plays a significant role in managing gout. Foods rich in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and alcohol, can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout flare-ups. Limiting these foods, along with maintaining a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, can help control uric acid levels and prevent complications.

Drinking plenty of water is also crucial, as it helps flush out excess uric acid from the body and supports kidney health. Staying hydrated can reduce the risk of kidney stones and improve overall gout management.
- Regular Exercise and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing gout and preventing its complications. Being overweight can increase the risk of developing gout and can make flare-ups more severe. Regular physical activity, combined with a healthy diet, can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of gout flare-ups.
- Avoid Dehydration
Dehydration can lead to a buildup of uric acid in the body, making gout attacks more likely. Ensuring you drink enough water throughout the day helps dilute uric acid and prevents the formation of urate crystals in the joints and kidneys. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, especially if you are at risk of gout or kidney stones.
Conclusion
Gout is not just a painful condition – it can lead to severe complications that affect your joints, kidneys, heart, and overall health. From joint damage and deformities to kidney stones and cardiovascular disease, the consequences of untreated gout are far-reaching. Early diagnosis, proper medication, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes can help prevent these dangerous complications and allow you to manage gout effectively.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gout or are at risk for the condition, don’t wait to seek help. Take control of your health today to avoid the serious complications that can result from ignoring the warning signs of gout.
If you or someone you know is suffering from gout, it’s important to take action and manage the condition before complications arise. Learn more about how to control your gout symptoms and protect your health by visiting our website for additional resources, advice, and support. Let’s work together to reduce the impact of gout on your life!
Leave a Reply