Cancer is a leading health concern worldwide, affecting millions of lives each year. Knowing the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and understanding preventive measures are key to reducing risks and improving outcomes. While cancer can be a complex disease with multiple causes, early detection can significantly increase survival rates.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of cancer, its most common causes, early symptoms to watch for, and practical tips for early detection. With heightened awareness and a proactive approach, individuals can play an active role in their health and potentially reduce the impact of this life-altering disease.
1. What is Cancer? An Overview of the Disease
Cancer is a broad term for a variety of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These rogue cells, if left unchecked, invade surrounding tissues and may spread to other parts of the body through a process called metastasis. Unlike healthy cells, which have specific functions and growth limits, cancer cells continue to divide and form masses, or tumors, which can interfere with normal bodily functions.
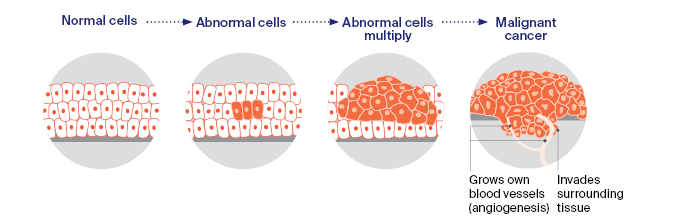
There are more than 100 types of cancer, affecting different tissues and organs, each with unique traits, risk factors, and treatment options. Common forms include breast cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and skin cancer. While cancer can occur in nearly any part of the body, understanding its causes and risks is crucial for both prevention and management.
2. Primary Causes of Cancer: Understanding Risk Factors
The exact causes of cancer are often multifaceted, with both environmental and genetic components playing a role. Here are some common risk factors that contribute to cancer development:
- Genetics: Family history and genetic predisposition can increase the risk of certain cancers, such as breast or colorectal cancer. Genetic mutations, whether inherited or acquired, may predispose individuals to specific types.
- Lifestyle Choices: Habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor dietary choices significantly increase cancer risk. For example, tobacco is a leading cause of lung cancer, while excessive alcohol intake has been linked to liver and throat cancers.
- Environmental Exposure: Long-term exposure to harmful substances like asbestos, radiation, and certain chemicals can lead to various cancers. Occupational hazards in certain industries can also contribute to higher risk.
- Infections: Certain viral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B and C, are associated with cancers like cervical and liver cancer. These infections alter cell behavior, increasing the likelihood of cancerous growths.
- Age and Immune System Health: As people age, the risk of developing cancer increases due to cumulative cell damage over time. A weakened immune system, whether due to age or medical conditions, can also heighten cancer susceptibility.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cancer-causes-513773_FINAL-ed7f995b3eca46eca8064643b15ce581.jpg)
Understanding these causes and managing controllable risk factors are essential for cancer prevention.
3. Recognizing Cancer Symptoms: Early Warning Signs to Note
Detecting cancer in its early stages is crucial for successful treatment, as it allows for intervention before the disease progresses. While symptoms vary widely depending on the type and stage of cancer, some general warning signs are common across many types:

- Unexplained Weight Loss: A sudden and unintentional weight loss of 10 pounds or more could be an early indicator of cancers such as lung, stomach, or pancreatic cancer.
- Persistent Fatigue: While fatigue can result from various factors, cancer-related fatigue does not improve with rest and may be accompanied by other symptoms.
- Pain: Pain that does not go away, particularly in the back or abdomen, can signal cancers like bone or ovarian cancer. Persistent headaches, too, may be a warning sign.
- Changes in Skin: Noticeable changes, such as yellowing, darkening, or excessive redness, may indicate skin cancer or cancers that affect liver function.
- Lumps or Swelling: Any unusual lump in the body, particularly in areas like the breast, testicles, or lymph nodes, should be examined by a healthcare provider, as it may signal a tumor.
- Persistent Cough or Hoarseness: Coughing or hoarseness that lasts more than three weeks could be related to cancers of the lung, throat, or thyroid.
- Bleeding or Discharge: Unexpected bleeding, such as in the stool, urine, or from unusual body openings, can indicate cancers of the colon, bladder, or reproductive organs.
While these symptoms may not always indicate cancer, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any persistent changes in your health.
4. The Importance of Early Detection in Cancer Treatment
Early detection is one of the most effective ways to combat cancer and increase survival rates. By identifying cancer in its initial stages, individuals can undergo treatment before the disease progresses, improving the chances of a full recovery. Here’s why early detection matters:
- Higher Survival Rates: Studies show that survival rates are significantly higher when cancer is detected and treated early.
- Less Aggressive Treatment: Early-stage cancers often require less invasive treatment options, reducing side effects and recovery time.
- Better Quality of Life: With early detection, patients can begin treatment before cancer disrupts daily life and general health, maintaining a better quality of life.
The benefits of early detection underscore the importance of regular screenings and being vigilant about health changes. By addressing symptoms and undergoing routine exams, individuals can catch potential health issues before they become severe.
5. Early Detection Tips: Screening and Preventive Measures

While some cancers do not exhibit noticeable symptoms in the early stages, regular screening and preventive health measures can aid in early detection. Here are some tips for proactive health monitoring:
- Routine Screenings: Regular screenings, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap smears, are essential for detecting cancers in their initial stages. For example, a colonoscopy can detect colorectal cancer early, and mammograms are critical for breast cancer detection.
- Self-Examinations: Self-checks, such as monthly breast and skin exams, help individuals spot changes, lumps, or abnormalities early on. Look for changes in size, shape, or color in moles or lumps.
- Annual Health Check-ups: Routine health visits allow for timely blood tests, physical exams, and discussions of any new symptoms. Annual check-ups can help detect underlying health issues before they progress.
- Genetic Testing: For those with a family history of cancer, genetic testing can reveal predispositions to certain cancers, allowing for a personalized prevention plan.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco, and limiting alcohol are all preventive measures that can lower cancer risk. A healthy lifestyle supports the immune system and reduces the chances of cell damage.
Taking proactive steps with these tips can increase your chances of detecting cancer at an early stage, contributing to better health outcomes.
6. Promising Advancements in Cancer Treatment and Research
In recent years, advances in cancer research have led to new and promising treatments, offering hope to patients and families. From immunotherapy to targeted therapy, these innovations aim to treat cancer more effectively and with fewer side effects:
- Immunotherapy: This approach harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells, with treatments like checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy showing success in cancers like melanoma and leukemia.
- Targeted Therapy: Unlike traditional treatments, targeted therapy focuses on specific cancer cells, minimizing harm to healthy tissue. This approach is effective in various cancers, including lung and breast cancer.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genetic testing allow for treatment tailored to an individual’s specific genetic makeup, improving effectiveness and minimizing side effects.
- Precision Surgery: Minimally invasive surgeries, such as robotic-assisted procedures, allow for precise tumor removal, reducing recovery time and improving outcomes.
These advancements are paving the way for more effective treatments, and ongoing research continues to explore new solutions for a variety of cancer types.
Conclusion: The Role of Awareness in Cancer Prevention
Understanding cancer, its causes, symptoms, and early detection strategies is essential for taking control of your health. While cancer can be a daunting diagnosis, early awareness and proactive health measures offer individuals a fighting chance. Through routine screenings, lifestyle choices, and staying informed on treatment advancements, anyone can reduce their risk and improve their outcomes.
By fostering awareness and encouraging early action, we can collectively work toward a future with fewer cancer diagnoses and more survivors.
Leave a Reply